
Galleri cancer test: What is it and who can get it?
It's hoped the Galleri test can detect more than 50 types of the disease before symptoms appear.
What is the Galleri cancer test?
It's a simple blood test that looks for the earliest signs of cancer, particularly those that are typically difficult to identify early or for which there are no NHS screening programmes - such as lung, pancreas or stomach cancers.
Developed by Californian firm Grail - and already used in the US - the test can detect subtle changes caused by cancers, when patients may have no other obvious symptoms.
It works by finding chemical changes in fragments of genetic code - cell-free DNA (cfDNA) - that leak from tumours into the bloodstream.
The signal does not mean that a person definitely has cancer. It just means that they might have cancer, and that they will need to have some follow-up tests to check.
"This quick and simple blood test could mark the beginning of a revolution in cancer detection and treatment here and around the world," says NHS England's Chief Executive Amanda Pritchard.
How will the trial work?
Participants will be asked to give a blood sample at a locally based mobile clinic.
They will then be invited back twice - after 12 months and two years - to give further samples.
Half those taking part will have their blood screened with the Galleri test immediately.
However, others will simply have their samples stored away to be tested in the future - should they go on to be diagnosed with cancer.
This is because the trial is what's known as a Randomised Control Trial (RCT).
It will allow scientists to see whether cancer is detected significantly earlier among people who have their blood tested straight away.
Will participants know if their blood has been tested?
People will only know they're in the first test group if they are among the small minority whose blood test detects potential signs of cancer.
Those people will be contacted by the trial nurses by phone and referred to an NHS hospital for further tests.
Everyone taking part will be advised to continue with their standard NHS screening appointments and to still contact their GP if they notice any new or unusual symptoms.
Who can volunteer for the NHS-Galleri trial?
The trial aims to recruit 140,000 volunteers across England.
But only people living in these areas can take part and they must be invited:
* Cheshire and Merseyside
* Cumbria
* Greater Manchester
* the North East
* West Midlands
* East Midlands
* East of England
* Kent and Medway
* South East London
Letters have already been sent to tens of thousands of people asking them to take part.
Those being asked are aged between 50 and 77, from a range of backgrounds and ethnicities, and must not have had a cancer diagnosis in the past three years.
What is the aim of the trial?
The NHS hopes the blood tests will help increase five-year survival rates for cancer, which are below the levels seen in many other high-income countries.
Developing a blood test for cancer has been keeping scientists busy for many years without much success.
Making one that's accurate and reliable has proved incredibly complex. The danger is that a test doesn't detect a person's cancer when they do have it, or it indicates someone has cancer when they don't.
"The test could be a game-changer for early cancer detection," says Prof Peter Sasieni, one of the trial's lead investigators. But he adds a note of caution:
"Cancer screening can find cancers earlier when they are more likely to be treated successfully, but not all types of screening work."
What difference could it make to cancer patients?
Patients whose cancers are found early - known as stage one or two - typically have a broader range of treatment options available to them, which can often be less aggressive.
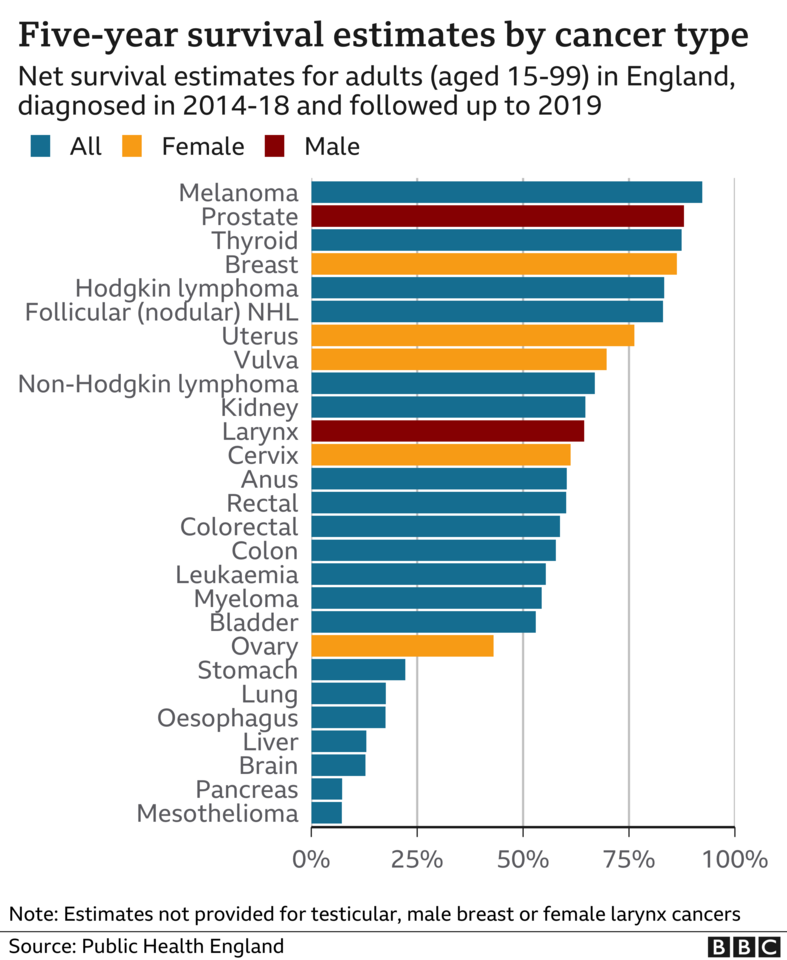
NHS England says a patient diagnosed at the earliest stage typically has between five and 10 times the chance of surviving compared with those found at the more advanced stage four.
Initial results from the Galleri study are expected by 2023. If successful, the NHS in England plans to extend the rollout to a further one million people in 2024 and 2025.










