
How much money is the UK government borrowing, and does it matter?
To bridge this gap it borrows money, but this is paid back - with interest.
Why does the government borrow money?
The government gets most of its income from taxes. For example, workers pay income tax, everyone pays VAT on certain goods and companies pay tax on their profits.
It could, in theory, cover all of its spending from taxes, and in some years that happens.
But if it can't, it needs to either raise taxes, cut spending or borrow.
Higher taxes mean people have less money to spend, so businesses make less profit, which can be bad for jobs and wages. Lower profits also mean companies pay less tax.
So, governments often borrow to boost the economy. They also borrow to pay for big projects - such as new railways and roads - which it also hopes will help the economy.
 Governments borrow to fund "day-to-day" spending, as well as long-term infrastructure projects like Crossrail
Governments borrow to fund "day-to-day" spending, as well as long-term infrastructure projects like Crossrail
How does the government borrow money?
The government borrows money by selling financial products called bonds.
A bond is a promise to pay money in the future. Most require the borrower to make regular interest payments over the bond's lifetime.
UK government bonds - known as "gilts" - are normally considered very safe, with little risk the money will not be repaid.
Gilts are mainly bought by financial institutions in the UK and abroad, such as pension funds, investment funds, banks and insurance companies.
The Bank of England has also bought hundreds of billions of pounds' worth of government bonds in the past to support the economy, through a process called "quantitative easing".
How much is the UK government borrowing?
The amount the government borrows varies from month to month.
When people submit tax returns In January, often paying a large chunk of their annual tax bill in one go, the government sees a jump in the amount of money it takes in.
So it is more helpful to look at the whole year, or the year-to-date.
In the 2022-23 financial year, the government borrowed £139.2bn. That was up by about 15% from last year.
The total amount the government owes is called the national debt. It is currently just over £2.5 trillion.
That is roughly the same as the value of all the goods and services produced in the UK in a year, known as the gross domestic product, or GDP.
That current level is more than double what was seen from the 1980s through to the financial crisis of 2008.
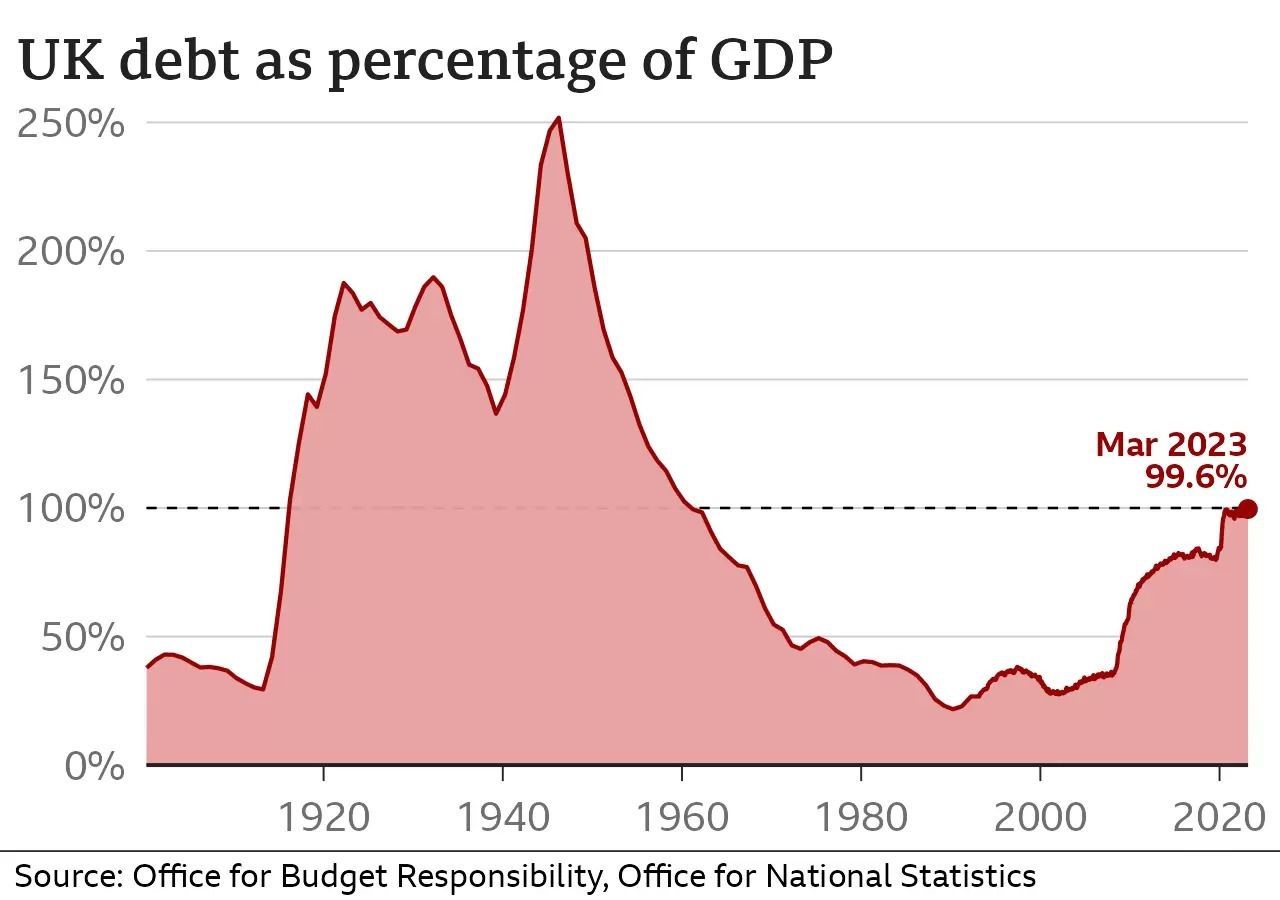
The combination of the financial crash and the Covid pandemic pushed the UK's debt up from those historic lows to its current level.
But in relation to the size of the economy, today's debt is still low compared with much of the last century, as shown above, and also compared with many leading advanced economies.
Why does it matter if governments borrow more?
The larger the national debt gets, the more interest the government has to pay.
That extra cost was not as big when the interest rates due were low through the 2010s. But it is more noticeable now that interest rates have risen.
Two months in 2022 saw record levels of money set aside for debt interest: £20bn in June and £18bn in December.
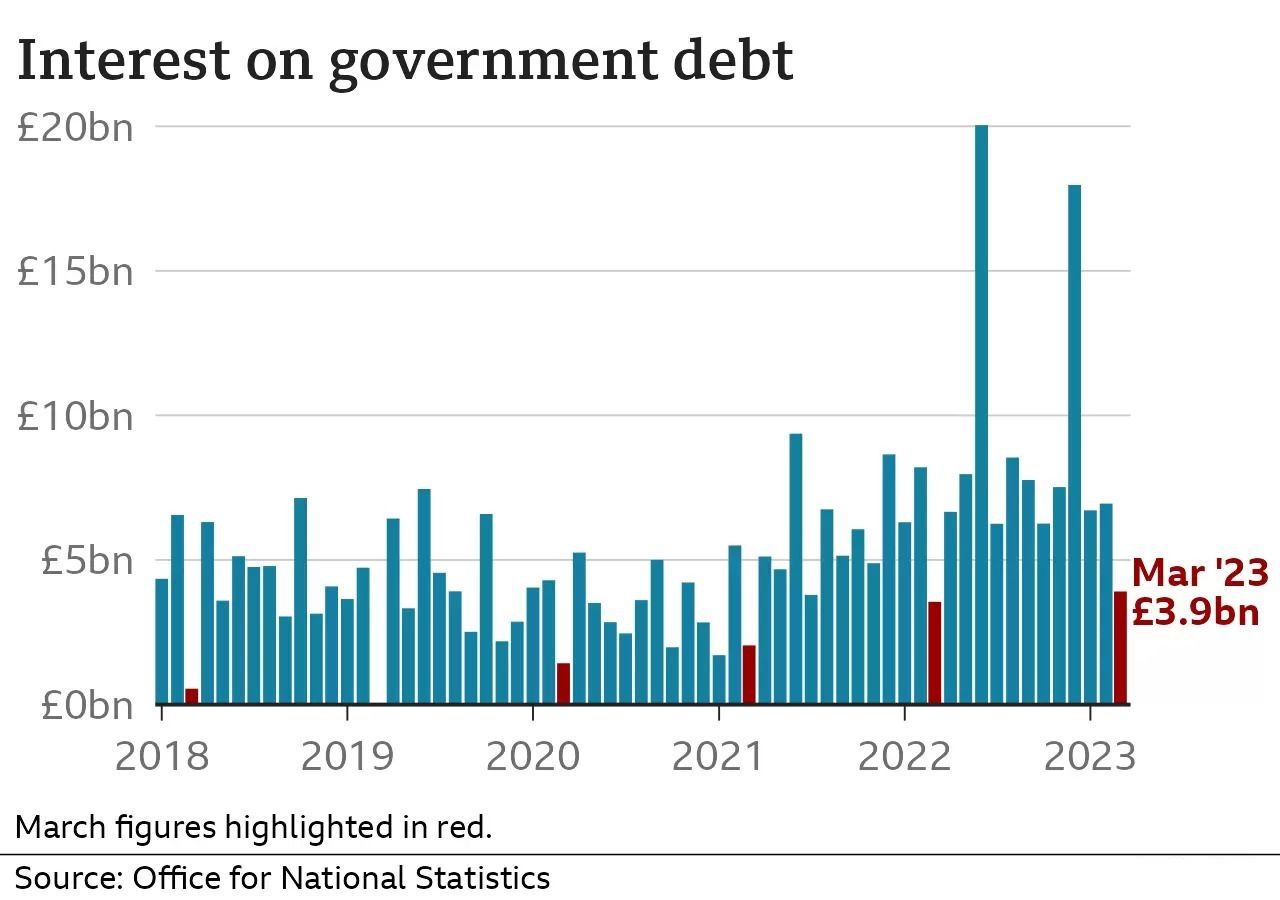
During the last financial year, the government put aside £106.6bn on debt interest - more than it spends on education.
Some economists fear the government is borrowing too much, at too great a cost.
Others argue extra borrowing helps the economy grow faster - generating more tax revenue in the long run.
What is the government's plan for debt?
Most economists and politicians agree that debt cannot keep growing compared to the size of the economy forever, because at some point it becomes impossible to pay the interest.
But there is debate about whether or how fast to cut borrowing.
Growing the economy is another way to bring down the main measure of the total national debt: its size compared to GDP.
Governments often increase borrowing when they face unusually difficult situations, such as the coronavirus pandemic, or the current cost-of-living crisis.
Chancellor Jeremy Hunt has blamed the "twin global emergencies of a pandemic and Putin's war in Ukraine" for driving up government costs.
He has said it is "vital [that] we stick to our plan to reduce debt over the medium term".
Prime Minister Rishi Sunak also made reducing the national debt one of his five key promises.
What is the difference between the government deficit and debt?
The deficit is the gap between the government's income and the amount it spends.
When a government spends less than its income, it has what is known as a surplus.
Debt is the total amount of money owed by the government that has built up over years.
It rises when there is a deficit, and falls in those years when there is a surplus.










