
Scientists sniff for hidden methane leaks to combat global warming
Methane leaks are the focus of new efforts to slow the pace of global warming. The colourless and odourless gas is an astonishing 84 times more potent in heating our atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 20 year period. However, finding and fixing leaks - be they from distant pipelines or city sewage systems - can be challenging.
To find out more, we joined a group of scientists from the University of Utrecht who are developing new methane-detecting methods in this episode of Climate Now.
Record-breaking heat
Before that report, however, let's look at the latest data from the Copernicus Climate Change Service, which reveals that Europe just had its warmest summer on record.
Temperatures from June to August this year were almost one degree Celsius above the 1991-2020 average. That puts 2021 marginally ahead of the previous warmest summers of 2010 and 2018.
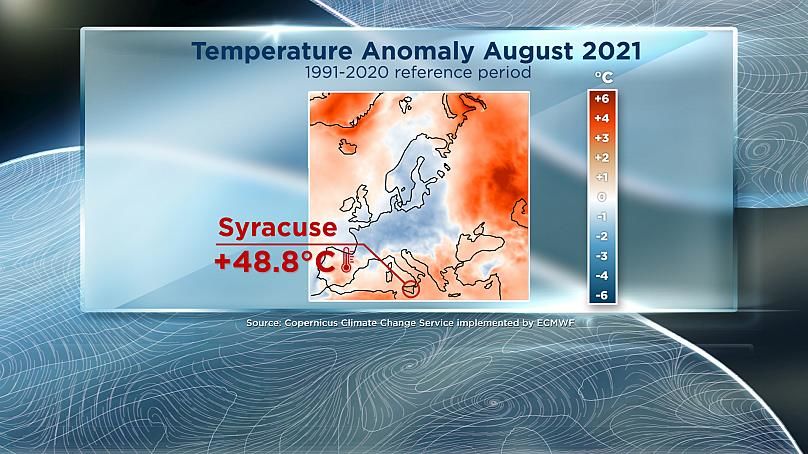
In the month of August itself, the Copernicus map of temperature anomalies across Europe shows the continent divided in two. Along the south and east, there was a sustained heatwave. The city of Syracuse in Sicily hit 48.8 degrees on the 11th of August. This temperature – if verified by the WMO – will be the highest temperature ever recorded in Europe.
The heatwave that hit Sicily was related to anticyclonic weather conditions, and was also linked to higher than average temperatures in north Africa, Greece, and Turkey. The mercury also soared several degrees above average to the north of the Caspian Sea and into Siberia.
However, from France across to Ukraine and Scandinavia temperatures were one or even two degrees lower than average last month.
The hunt for methane
The IPCC report last month called for a big effort to reduce methane emissions from industrial sources.
There are two broad approaches to finding methane leaks, One involves employing data from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite and computer models of the atmosphere to find unexpected sources of methane from oil and gas plants.
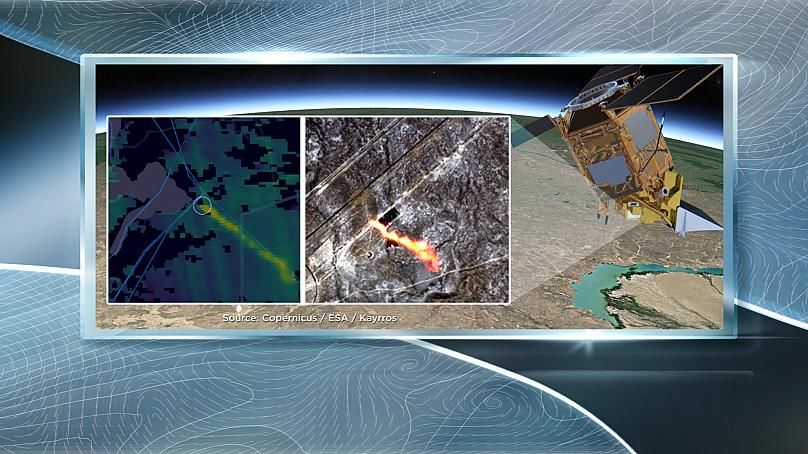

The other approach is much more down-to-earth, and involves literally searching for methane street by street, as Euronews discovered in Utrecht.
We were invited to join scientists Hossein Maazallahi and Hanne Notø as they set off for a routine drive around their home city to hunt for the colourless, odorless gas using their specialist equipment.
An Iranian PhD student at the University of Utrecht, Hossein, tells us that their specialised tools are constantly sampling the air from the air intake on their vehicle. Due to the instrument's high sensitivity, they can identify leaks that may never have been spotted with older equipment or techniques.
"If you have one billion molecules in the air and one of them is methane, these instruments can detect that," he tells Euronews.
Leaks in unexpected places
The day we follow the pair, they find several methane plumes, the first coming from an underground gas pipe. Such leaks can sometimes go on for months or even years undetected. However, as we pass along a residential street close to a roundabout the instruments suddenly pick up a signal. Hossein's methane-measuring devices registered a jump in CH4 in the atmosphere from 2 to 1000 PPM.
One thousand parts per million is 500 times higher than usual levels. The methane leak is thus confirmed.

Norwegian PhD student Hanne explains that the protocol is to then take an air sample back to the lab for further analysis. This way they can "discover what the source of the leak is."
They continue their search, and again, on a normal residential street, their instruments show a slight spike in the signal. We walk up and down the road with the gas sampling nozzle close to the cracks in the road. Greenhouse gases are indeed leaking out of a pipeline somewhere underground between the houses and the canal, but it's tricky to say exactly where.
The team pauses again to take a third sample when they spot a broad methane plume- at least 100 metres across - with a rather low concentration of gas. The source isn't exactly unexpected, it's a wastewater treatment plant for the town, and although the gas is diffuse in this area it's actually a comparatively large net source of greenhouse gas.
The methane from such facilities is produced by natural processes, and can actually be captured and used as a source of fuel with the correct modifications to the plant.
Hossein explains that their priority in this work is to not only find the leaks, but also quantify them, in order to build a ranking of the biggest emission sources and inform utilities and city authorities.
Checking the 'chemical fingerprints'
The samples are finally taken to colleagues in the university lab to measure the isotopes in the gas - these readings show the 'chemical fingerprints' in the methane, and will reveal if the source is from domestic gas for heating and cooking, or other biogenic processes.
The research team's goal is for their fast and highly sensitive methane-sniffing technology to be widely deployed to find and fix previously invisible leaks
Leading the researchers is Professor of atmospheric physics and chemistry, Thomas Röckmann, who explains their efforts to find and fix the leaks: "Methane is the second most important greenhouse gas and it's one of the prime options now for reducing the climate impact of humans," he says.
Many of the large methane leaks from the oil and gas industry come from large plants, and can be fixed using existing methods. However, the smaller leaks that his team can now find have not historically been a priority. Röckmann believes that will change.
"Methane has been identified now clearly by the recent IPCC report, and our policy and industry also picked this up," he says. "We have to do everything we can. We have to target every activity in human life that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions."
He says their lab-scale techniques will first need to be scaled up and integrated with the workflows of gas companies, but they have a lot of potential. "We can go around, we can cover entire cities in a short moment. We can find and fix the leaks together with utilities and therefore contribute to reducing these emissions," he says.
Given methane's warming effect on our climate, it could have a powerful impact. "A recent scientific study has shown that it's possible to reduce methane emissions by 50 percent by the year 2030. And if you do that, we can prevent warming of a quarter degree by the middle of this century and even half a degree by 2100. And this would be really a significant fraction of the warming that we are expecting," Röckmann concludes.










