
New Bluetooth hack can unlock your Tesla—and all kinds of other devices
When you use your phone to unlock a Tesla, the device and the car use Bluetooth signals to measure their proximity to each other. Move close to the car with the phone in hand, and the door automatically unlocks. Move away, and it locks. This proximity authentication works on the assumption that the key stored on the phone can only be transmitted when the locked device is within Bluetooth range.
Now, a researcher has devised a hack that allows him to unlock millions of Teslas—and countless other devices—even when the authenticating phone or key fob is hundreds of yards or miles away. The hack, which exploits weaknesses in the Bluetooth Low Energy standard adhered to by thousands of device makers, can be used to unlock doors, open and operate vehicles, and gain unauthorized access to a host of laptops and other security-sensitive devices.
When convenience comes back to bite us
“Hacking into a car from hundreds of miles away tangibly demonstrates how our connected world opens us up to threats from the other side of the country—and sometimes even the other side of the world,” Sultan Qasim Khan, a principal security consultant and researcher at security firm NCC Group, told Ars. “This research circumvents typical countermeasures against remote adversarial vehicle unlocking and changes the way we need to think about the security of Bluetooth Low Energy communications.”
This class of hack is known as a relay attack, a close cousin of the person-in-the-middle attack. In its simplest form, a relay attack requires two attackers. In the case of the locked Tesla, the first attacker, which we’ll call Attacker 1, is in close proximity to the car while it’s out of range of the authenticating phone. Attacker 2, meanwhile, is in close proximity to the legitimate phone used to unlock the vehicle. Attacker 1 and Attacker 2 have an open Internet connection that allows them to exchange data.
Attacker 1 uses her own Bluetooth-enabled device to impersonate the authenticating phone and sends the Tesla a signal, prompting the Tesla to reply with an authentication request. Attacker 1 captures the request and sends it to Attacker 2, who in turn forwards the request to the authenticating phone. The phone responds with a credential, which Attacker 2 promptly captures and relays back to Attacker 1. Attacker 1 then sends the credential to the car.
With that, Attacker 1 has now unlocked the vehicle. Here’s a simplified attack diagram, taken from the above-linked Wikipedia article, followed by a video demonstration of Khan unlocking a Tesla and driving away with it, even though the authorized phone isn’t anywhere nearby.
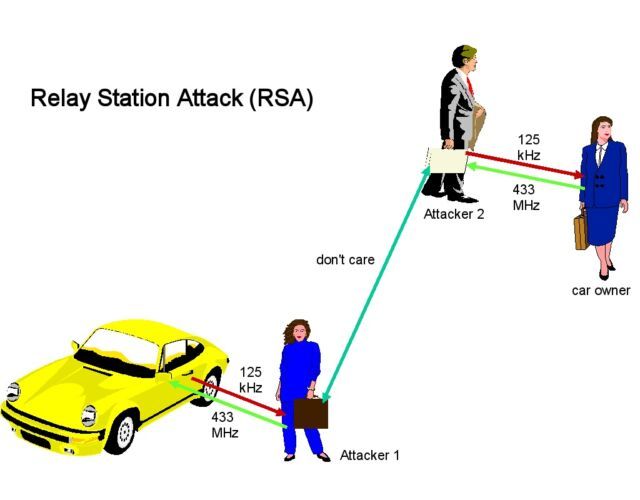
Relay attacks in the real world need not have two actual attackers. The relaying device can be stashed in a garden, coat room, or other out-of-the-way place at a home, restaurant, or office. When the target arrives at the destination and moves into Bluetooth range of the stashed device, it retrieves the secret credential and relays it to the device stationed near the car (operated by Attacker 1).
The susceptibility of BLE, short for Bluetooth Low Energy, to relay attacks is well known, so device makers have long relied on countermeasures to prevent the above scenario from occurring. One defense is to measure the flow of the requests and responses and reject authentications when the latency reaches a certain threshold, since relayed communications generally take longer to complete than legitimate ones. Another protection is encrypting the credential sent by the phone.
Khan’s BLE relay attack defeats these mitigations, making such hacks viable against a large base of devices and products previously assumed to be hardened against such attacks.
On the (link) level
The key to the successful bypass is that, unlike previous BLE relay attacks, it captures data from the baseband—where radio signals are sent to and received from the devices—and does so at the link layer, the very lowest level of the Bluetooth stack, where connections are advertised, created, maintained, and terminated. Previous BLE relay attacks worked at the GATT—short for Generic Attribute Profile—layer, which is much higher up the stack.
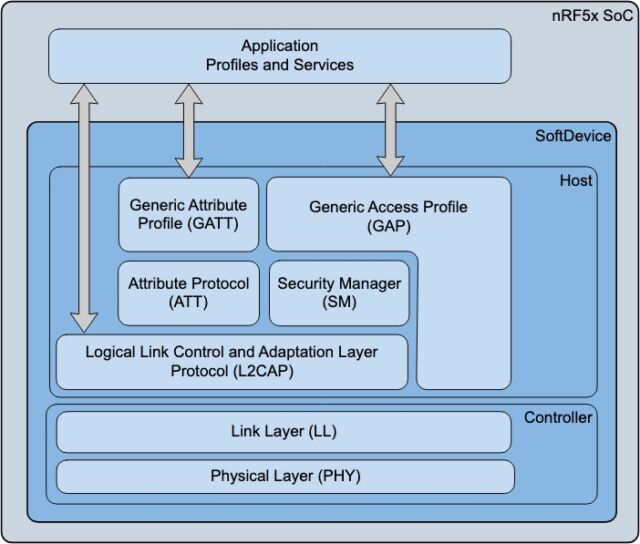
Because the link layer is where the credential is encrypted, the new method defeats cryptographic defenses that defend against GATT-based relays. Link layer relays also have significantly less latency than GATT relays because they bypass levels higher up the stack that act as a bandwidth bottleneck. That makes link layer relays indistinguishable from legitimate communications.
Khan’s attack uses custom software and about $100 worth of equipment. He has confirmed it works against the Tesla Model 3 and Model Y and Kevo smart locks marketed under the Kwikset and Weiser brand names. But he says virtually any BLE device that authenticates solely on proximity—as opposed to also requiring user interaction, geolocation querying, or something else—is vulnerable.
“The problem is that BLE-based proximity authentication is used in places where it was never safe to do so,” he explained. “BLE is a standard for devices to share data; it was never meant to be a standard for proximity authentication. However, various companies have adopted it to implement proximity authentication.”
Because the threat isn’t caused by a traditional bug or error in either the Bluetooth specification or an implementation of the standard, there’s no CVE designation used to track vulnerabilities. Khan added:
In general, any product relying on BLE proximity authentication is vulnerable if it does not require user interaction on the phone or key fob to approve the unlock and does not implement secure ranging with time-of-flight measurement or comparison of the phone/key fob’s GPS or cellular location relative to the location of the device being unlocked. GPS or cellular location comparison may also be insufficient to prevent short distance relay attacks (such as breaking into a home’s front door or stealing a car from the driveway, when the owner’s phone or key fob is inside the house).
Making BLE authentication safer
With no patch or fix in sight, what can be done? The answer: require something more than just perceived proximity before trusting the phone or key fob as authentic. One mechanism is to check the location of the authenticating device to ensure that it is, in fact, physically close to the locked car or other device.
Another countermeasure is to require the user to provide some form of input to the authenticating device before it’s trusted. Phone-based security keys that comply with the recently introduced WebAuthn standard, for instance, require not only that the device be close to the machine or account being unlocked but also that a user present the device with a valid fingerprint, facial scan, or PIN. That prevents this attack from working on those devices.
Another countermeasure is to use a phone’s accelerometer to measure its movements. When a device has been stationary for a given amount of time, the proximity key functionality is disabled.
A Kwikset representative said that its iOS app for Kevo has a timeout feature that activates once a device has been stationary for 30 seconds. It also provides an option for requiring a PIN before the device is trusted. Those features aren’t yet available in the company’s Android app. The representative said the company expects the PIN option to be available in the Android app by late September. The attack works only on Kwikset’s Kevo line, the representative said.
Representatives of The Bluetooth Special Interest Group, the body that oversees the Bluetooth standard, issued a statement that read in part: “The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) prioritizes security, and Bluetooth specifications include a collection of features that provide developers the tools they need to secure communications between Bluetooth devices and implement the appropriate level of security for their products. All Bluetooth specifications are subject to security reviews during the development process.”
Tesla representatives didn’t respond to an email seeking comment for this article.
NCC Group issued a statement about the hack here and has published advisories here, here, and here.
In fairness to both the lock maker and electric car manufacturer, they are only two of the many device makers affected by this new attack. The point of the research isn’t to single out one or two offenders but rather to make clear that BLE authentication based on proximity alone was never something anticipated in the standard and should have been abandoned long ago.
“Over the last decade, industry has turned a blind eye to the risks of relay attacks against proximity authentication systems,” Khan said. “This research demonstrates that Bluetooth Low Energy relay attacks are practical and effective against popular products and highlights the need for the industry to rethink the risk-to-convenience tradeoff for Bluetooth passive entry.”










