
Is the UK-EU trade deal worth keeping?
Our view has always been that the deal offered only modest economic benefits, which will decline over time, and has significant economic and political downsides. Recent trade data strengthens this argument. If the deal ultimately has to go, the UK government should not be overly concerned.
We are not big fans of the UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA). After it was signed, we wrote that while it formed a reasonable basis for the restoration of Britain’s economic and political independence, it came with significant downsides.
We further argued that the UK government should be ready to quit the deal when it comes up for review in 2026 if those downsides make it even less attractive. We dubbed the TCA an ‘experimental peace’ in the full expectation that it would not be the start of a new and harmonious relationship between the UK and EU. We expected the EU behave aggressively towards the UK over various issues, using the threat of collapsing or narrowing the TCA.
Recent developments in Northern Ireland have confirmed our pessimistic predictions and raised doubts about the future of the TCA. The EU has threatened unspecified trade sanctions against the UK in response to the UK’s actual and putative unilateral actions to modify the Northern Ireland Protocol (NIP) and reduce its damaging effects on Northern Irish society.
Such sanctions would reduce the already modest economic benefits of the TCA, a relatively ‘thin’ trade deal which mostly focuses on eliminating tariff barriers that would otherwise exist between the UK and the EU. Importantly, these tariff barriers would not be large. The weighted average tariff on UK exports to the EU would be around 3.5%. Around 70% of UK exports would face tariffs of just 0-2% with only 7% facing tariffs of 10% or more (data based on 2-digit industry sectors). High tariffs would largely be in agriculture, a small export sector for the UK. For manufacturers, the average tariff would be 3% and just 2.1% for manufactured goods excluding autos (see Chart 1).
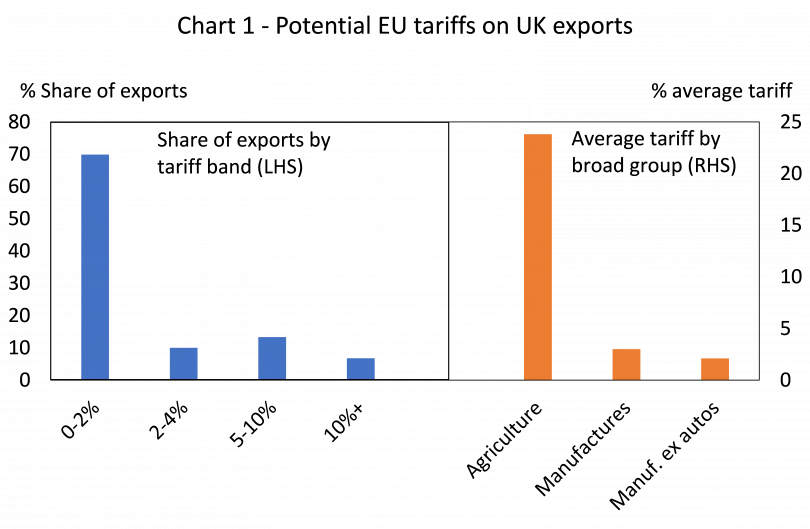
If UK exports were to face these tariffs, the economic losses would be modest. Based on a price elasticity of around 1.5, UK exports to the EU might fall by around £7 billion per year, which is equivalent to just 0.3% of UK GDP.
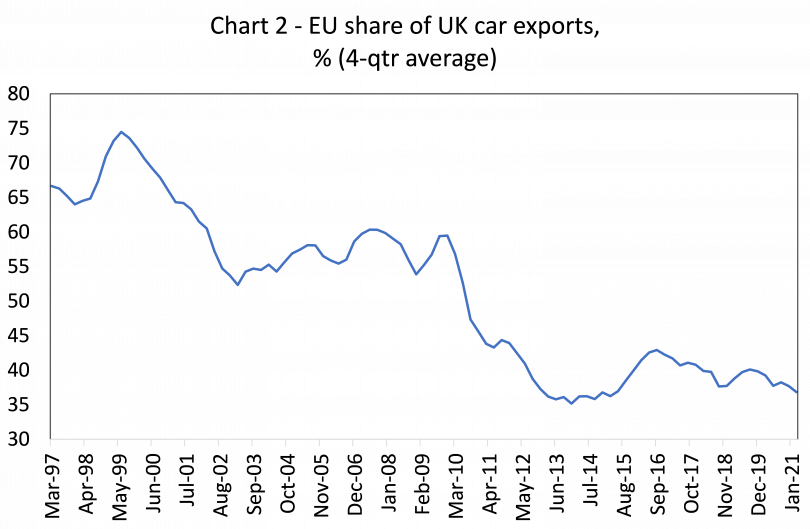
Certainly, there would be problems for some sectors where tariffs are higher, such as agriculture and motor vehicles. But agriculture is a small sector and the car sector might manage much better than many think. First, assuming the UK mirrored EU car tariffs, there would be a significant amount of import substitution as EU cars became more expensive – note the UK runs a large trade deficit with the EU in cars. Second, the EU is no longer the main market for UK car exports. Indeed, close to two-thirds of UK car exports by value now go to non-EU destinations (see Chart 2).
Exiting the TCA would not make much difference to levels of non-tariff barriers to trade with the EU, because the TCA – being a ‘thin’ trade deal – did little to remove these. Border frictions and regulatory issues would remain a fact of life.
But importantly, incoming trade data shows that the effect of these non-tariff barriers to trade is much smaller than many observers have claimed over the last several years – and UK exports are much more resilient to them. In May, UK non-food exports to the EU had recovered from their drop at the start of the year to stand at similar levels to those seen in the final months of 2020 i.e. just before the UK left the EU single market and customs union. Even food exports, by the far the most affected by EU trade barriers, were only about 1% below their October 2020 levels (Chart 3).
Exiting the TCA would also have little impact on UK services exports. The TCA didn’t offer much to services exporters, which (as we have consistently argued) never gained a huge amount from EU membership anyway. The resilience of UK services exports this year so far confirms this.
The trade outcomes this year are dramatically different from the massive losses predicted by the Treasury and various other bodies as a result of Brexit. It is likely that those predictions – and the lobbying they generated – played a big role in persuading the government to agree the TCA. That decision looks less surefooted in the light of the data so far.
Indeed, if we set possible trade losses (as calculated above) against potential gains from leaving the TCA, the balance looks attractive. It would make it easier for the UK government to dispense with the dreadful and damaging Northern Ireland Protocol. It would allow the UK government to take back a much larger share of UK fishing resources (worth several hundred million pound per year). It might even allow the UK to dispense with the massive EU exit bill to which it agreed in the naïve belief that it might build some goodwill with the EU side.
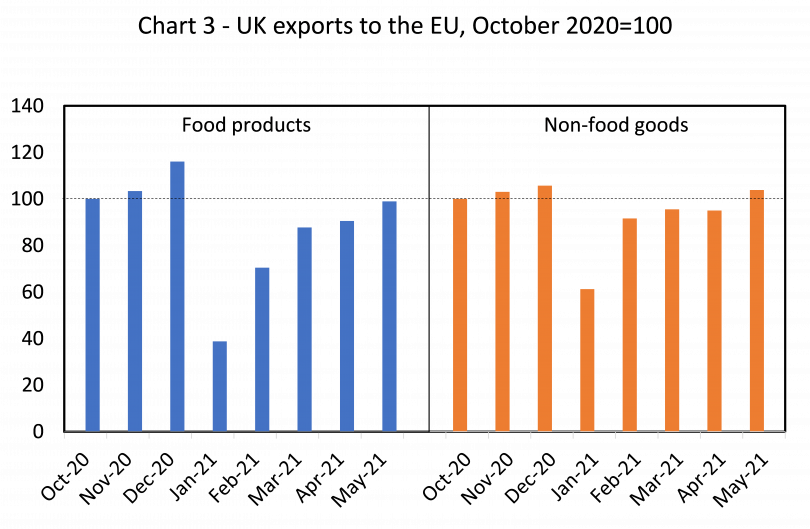
In any case, the TCA is likely to become increasingly less valuable to the UK over time. It is possible that some of its benefits may be cancelled by the EU’s moves to introduce a protectionist carbon border tax (which could also undermine still further the trade relationship between GB and Northern Ireland).
And crucially, the TCA will be facilitating a smaller and smaller share of total UK trade as the years progress. The share of EU markets in UK goods exports has already dropped from 56% in 1997 to 45% in 2019 and is set to fall considerably further. The EU share is falling because of the EU’s slow growth (less than half the pace of non-EU markets in the last twenty years) and because non-EU markets have absorbed more UK goods per unit of growth than EU markets (a higher income elasticity).
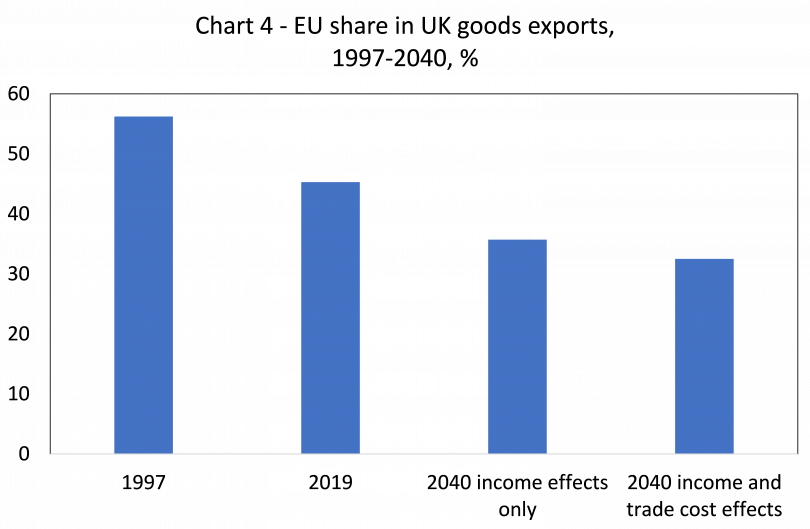
Based on long-term GDP growth forecasts for the EU and rest of the world, we estimate the share of UK goods going to the EU could drop to just 36% by 2024. If we also assume UK trade deals reduce trade barriers faced by UK exporters in the rest of the world by 3 percentage points (tariff equivalent), and that non-tariff barriers between the UK and EU due to Brexit are about 4% of trade values (and shrink bilateral trade accordingly), then the share of UK exports going to the EU might fall to just 33% by 2040 (see Chart 4).
The reality is that, with the EU running a massive goods trade surplus with the UK, it is the bigger winner from the TCA. It also got much of what it wanted in areas like fishing, a considerable amount on ‘level playing field’ issues and preserved the Northern Ireland Protocol – which for the UK is both economically damaging and constitutionally offensive. The UK made a lot of damaging concessions in return for very modest economic returns and should not be overly concerned about walking away from the TCA.











