
How cybercriminals collaborate to conduct ransomware attacks
Putin reportedly agreed in principle, but insisted that extradition be reciprocal. Time will tell if an extradition treaty can be reached. But if it is, who exactly should extradited – and what for?
The problem for law enforcement is that ransomware – a form of malware used to steal organisations’ data and hold it to ransom – is a very slippery fish. Not only is it a blended crime, including different offences across different bodies of law, but it’s also a crime that straddles the remit of different policing agencies and, in many cases, countries. And there is no one key offender. Ransomware attacks involve a distributed network of different cybercriminals, often unknown to each other to reduce the risk of arrest.
So it’s important to look at these attacks in detail to understand how the US and the G7 might go about tackling the increasing number of ransomware attacks we’ve seen during the pandemic, with at least 128 publicly disclosed incidents taking place globally in May 2021.
What we find when we connect the dots is a professional industry far removed from the organised crime playbook, which seemingly takes its inspiration straight from the pages of a business studies manual.
The ransomware industry is responsible for a huge amount of disruption in today’s world. Not only do these attacks have a crippling economic effect, costing billions of dollars in damage, but the stolen data acquired by attackers can continue to cascade down through the crime chain and fuel other cybercrimes.
Ransomware attacks are also changing. The criminal industry’s business model has shifted towards providing ransomware as a service. This means operators provide the malicious software, manage the extortion and payment systems and manage the reputation of the “brand”. But to reduce their exposure to the risk of arrest, they recruit affiliates on generous commissions to use their software to launch attacks.
This has resulted in an extensive distribution of criminal labour, where the people who own the malware are not necessarily the same as those who plan or execute ransomware attacks. To complicate things further, both are assisted in committing their crimes by services offered by the wider cybercrime ecosystem.
How do ransomware attacks work?
There are several stages to a ransomware attack, which I have teased out after analysing over 4,000 attacks from between 2012 and 2021.
First, there’s the reconnaissance, where criminals identify potential victims and access points to their networks. This is followed by a hacker gaining “initial access”, using log-in credentials bought on the dark web or obtained through deception.
Once initial access is gained, attackers seek to escalate their access privileges, allowing them to search for key organisational data that will cause the victim the most pain when stolen and held to ransom. This is why hospital medical records and police records are often the target of ransomware attacks. This key data is then extracted and saved by criminals – all before any ransomware is installed and activated.
Next comes the victim organisation’s first sign that they’ve been attacked: the ransomware is deployed, locking organisations from their key data. The victim is quickly named and shamed via the ransomware gang’s leak website, located on the dark web. That “press release” may also feature threats to share stolen sensitive data, with the aim of frightening the victim into paying the ransom demand.
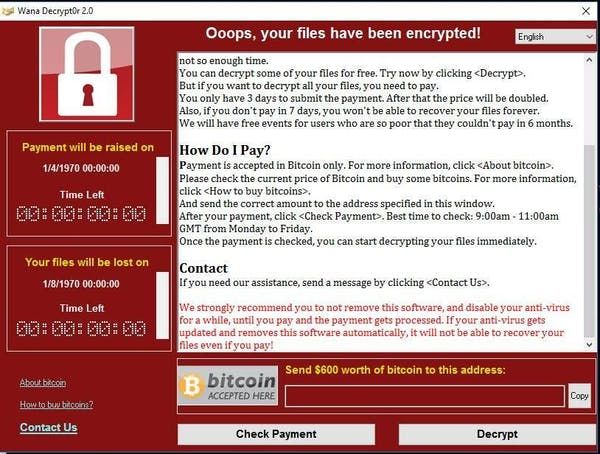 Victims of ransomware attacks are typically presented with a screen like this.
Victims of ransomware attacks are typically presented with a screen like this.
Successful ransomware attacks see the ransom paid in cryptocurrency, which is difficult to trace, and converted and laundered into fiat currency. Cybercriminals often invest the proceeds to enhance their capabilities – and to pay affiliates – so they don’t get caught.
The cybercrime ecosystem
While it’s feasible that a suitably skilled offender could perform each of the functions, it’s highly unlikely. To reduce the risk of being caught, offender groups tend to develop and master specialist skills for different stages of an attack. These groups benefit from this inter-dependency, as it offsets criminal liability at each stage.
And there are plenty of specialisations in the cybercrime underworld. There are spammers, who hire out spamware-as-a-service software that phishers, scammers, and fraudsters use to steal people’s credentials, and databrokers who trade these stolen details on the dark web.
They might be purchased by “initial access brokers”, who specialise in gaining initial entry to computer systems before selling on those access details to would-be ransomware attackers. These attackers often engage with crimeware-as-a-service brokers, who hire out ransomware-as-a-service software as well as other malicious malware.
To coordinate these groups, darkmarketeers provide online markets where criminals can openly sell or trade services, usually via the Tor network on the dark web. Monetisers are there to launder cryptocurrency and turn it into fiat currency, while negotiators, representing both victim and offender, are hired to settle the ransom amount.
This ecosystem is constantly evolving. For example, a recent development has been the emergence of the “ransomware consultant”, who collects a fee for advising offenders at key stages of an attack.
Arresting offenders
Governments and law enforcement agencies appear to be ramping up their efforts to tackle ransomware offenders, following a year blighted by their continued attacks. As the G7 met in Cornwall in June 2021, Ukrainian and South Korean police forces coordinated to arrest elements of the infamous CL0P ransomware gang. In the same week, Russian national Oleg Koshkin was convicted by a US court for running a malware encryption service that criminal groups use to perform cyberattacks without being detected by antivirus solutions.
While these developments are promising, ransomware attacks are a complex crime involving a distributed network of offenders. As the offenders have honed their methods, law enforcers and cybersecurity experts have tried to keep pace. But the relative inflexibility of policing arrangements, and the lack of a key offender (Mr or Mrs Big) to arrest, may always keep them one step behind the cybercriminals – even if an extradition treaty is struck between the US and Russia.










