
China puts shackles on fintech as technology risks usurping finance
Late at night on Monday November 2, a blog appeared in the official Sina.com account of the Chinese government’s mouthpiece news agency Xinhua, hours after regulators summoned executives of the world’s largest fintech company to tell them that the rules governing their industry were evolving.
Using the pseudonym Xiuxin, the blogger told a story about the potential harm that could be done by loose words, unrestrained behaviour and indiscretion, accompanied by an artwork showing a white horse afloat in a sea of clouds, an allusion to the Chinese name of one of China’s wealthiest men, Jack Ma.
A day later, the blog’s implication became apparent. Regulators did the unthinkable: pulling the rug from under the largest capital raising exercise in global finance – the US$35 billion initial public offering in Hong Kong and Shanghai by Ant Group– 48 hours before trading was due to start, citing changes in regulatory environment that cause the fintech giant to be in breach of market disclosure rules.

The new rules are part of regulators’ attempts to redefine and rethink fintech, amid concerns that technology has usurped the fundamentals of finance, creating potential systemic risks in the world’s second-largest economy.
“Chinese fintech groups have, in some cases, grown so big that their collaborations with banks are increasing contagion risks in China’s financial system,” said Grace Wu, an analyst at Fitch Ratings. “We expect tighter regulations on fintech companies to continue.”
What constitutes fintech is quietly being argued over in China, the world’s largest fintech market, where physical cash is hardly used in daily life and cashless mobile payments topped US$14 trillion in the fourth quarter of 2019, according to the People’s Bank of China(PBOC).
The debate came to a head on October 24 at a Shanghai conference, where Ma, speaking to an audience of financial regulators and senior government officials, outlined a fintech vision that uses big data analysis, cloud computing and artificial intelligence algorithms to reduce financial risks, drawing a stark contrast to the collateralised form of bank lending he described as being akin to pawn shops.
But the excessive use of technology in finance – especially the little-understood mixture of big data, artificial intelligence and cloud computing – may be too potent for regulators who are wary of defaults and disruptions of financial services spilling over into social unrest.
The US-China conflict over trade and technology “is no longer the single biggest risk for investors in Chinese technology”, said TS Lombard’s China policy analyst, Eleanor Olcott.

“Dramatic as the suspension [of Ant’s dual listing] was, it forms part of a wider political drive as the leadership seeks to widen and consolidate its control over finance and technology as well as over other key sectors.”
As China transformed from an export-driven economy to one reliant on consumer spending over the past decade, fintech conglomerates rose to serve the country’s 11.8 trillion yuan (US$1.8 trillion) consumer loans market, creating new risks outside the tightly regulated banking system.
Until recently, fintech companies had been given room to roam, enabling lenders in China’s so-called shadow banking system to grow into some of the world’s most valuable companies.
These “big tech” firms, including the likes of JD Digits, Lufax, Ant Group, have become the top brass of China’s nonbank lenders attracting big cheques from international investors. Ant is an affiliate of Alibaba Group Holding, which owns South China Morning Post.
As internet giants and online lenders such as 360 Digitech, Lexin and Yiren Digital account for a much larger piece of China’s consumer loans, regulators are increasingly unnerved by their cosy relationship with banks in the trillions of yuan of loans extended to borrowers.
Their combined share may grow to a third of China’s 11.8 trillion yuan (1.8 trillion) consumer loan market this year, from 17 per cent in 2017, according to an April research note by China Renaissance.
Unlike other countries where nonbank lenders lean heavily on the capital markets to fund their businesses, nonbank players in China have to rely on traditional banks for capital to provide credit to borrowers. By letting them operate outside the formal banking system, a broader systemic risk is becoming increasingly palpable.
China’s household debt rose to more than 60 per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) over the past five years. While less than America’s first-quarter debt-to-GDP ratio at 75 per cent, the pace rivals the expansion of consumer borrowing in the US just before the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, the Rhodium Group said in May.
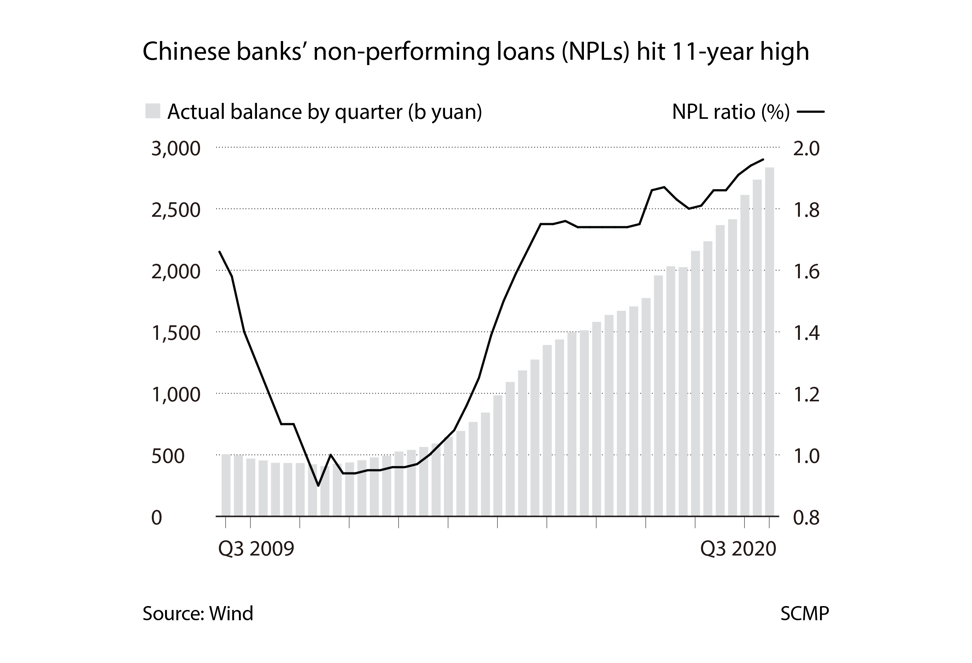
At the same time, the banking sector’s non-performing loans ratio rose to a 11-year high of 1.96 per cent in the third quarter. That marks the end of fat margins for fintech companies, as their activities are ring-fenced and they can no longer harvest the difference in rates off banks’ capital.
“We see an aggressive tightening over the past two years on China’s online lending, as some of the smaller banks have become more aggressive in their partnership with online platforms,” said Fitch’s Wu, adding that “banking systemic risks and household leverage are the issues at stake”.
Proposed rules in fintech, which would require lenders like Ant to pony up the equivalent of 30 per cent of their loans book in capital, may substantially change their business model of co-lending alongside banks.
The message from regulators is clear, said Liang Tao, vice-chairman of the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC). The regulator must group all financial activities from fintech firms under the same comprehensive ambit as banks, he said during a Beijing financial forum last week.
“Fintech has improved the efficiency of financial services, but it has not fundamentally changed the core nature of finance,” Liang said.

The draft rules for online micro loans were aimed at China’s legion of small banks, the so-called city and rural commercial banks which together hold 26 per cent of the sector’s assets in September, said Jefferies Hong Kong’s analyst, Chen Shujin.
These banks, many with weak capital buffers, are motivated by their partners’ ability to lend to individual borrowers across provincial boundaries: banks in the rural west or north are especially keen to lend to borrowers in the wealthy coastal areas, she said.
As banks essentially provide their balance sheets to back up online loans, any default could force the banks to book impairment losses – which, if serious, could trim their earnings and bite into their core capital.
“We expect slower growth in online microloans and lower profitability for loan facilitation businesses,” said Chen, adding that “regulators are cautious on high-yield consumer loans despite labels of inclusive financing or financial innovation.”

Signs already abound that indicate the central bank and other regulators are wary of how third-party payment networks such as Ant’s Alipay and Tencent’s
WeChat Pay are becoming almost too big to fail.
The two account for over 90 per cent of mobile payments and are deemed “systemically significant infrastructure” operators in China by some central bankers.
Regulators are also keen to protect the interests of state-owned banks, an important conduit for executing China’s economic policies.
Banks were asked to sacrifice as much as 1.5 trillion yuan (US$228 billion) in 2020 profits to finance cheap loans, cut fees and deferred repayments to help small businesses survive the coronavirus pandemic.
Regulators are hence keen to ensure that any innovation in the name of fintech does not compromise the banks’ role in safeguarding economic growth and stability.

That is why some of the fintech firms’ money market funds such as Ant’s Yu’e Bao, once the world’s largest with US$267 billion of assets in 2018, have also been targeted by regulators for downsizing due to their competition with banks’ deposits, said CMB International Securities’ analyst Terry Sun.
“If banks have to retain their deposit base, they will have to raise their deposit rates,” Sun said. “As banks ultimately have to protect their net interest margins, this would cause them to price their loan interest rates higher, affecting corporate borrowers.”
The new rules on micro loans – loans of typically less than 50,000 yuan (US$7,600) – follow a years-long effort by the Chinese government to cut China’s financial risk, known as deleveraging, to alleviate the buildup of bad debt caused by the massive spending spree by some its biggest private-sector companies.
Anbang Group, whose portfolio at one stage included the Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York and rural banks in China, was once one of the country’s most acquisitive companies until it was seized by Beijing in 2017, and its former chairman was jailed for fraud.
The company formally applied to disband in September and liquidate after selling much of its assets. HNA Group and Dalian Wanda Group are two other debt-laden conglomerates forced to sell off assets as part of the deleveraging purge.

Last year, Baoshang Bank became the first Chinese lender to be nationalised by regulators in two decades to contain its credit risk.
The lender was part of the business empire of the financier Xiao Jianhua, which ran into trouble after Xiao’s Tomorrow Group failed to repay billions of yuan in loans. Parts of Xiao’s empire were seized by authorities. The government also took over regional lenders Bank of Jinzhou and Shandong province’s Hengfeng Bank last year.
Another cause for concern: China’s biggest banks are reporting their first drop in profits since 2008 after they shored up their reserves for potential soured loans amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
The banking industry will have to dispose of 3.4 trillion yuan in non-performing loans this year, a dramatic increase from last year’s 2.3 trillion yuan, the bank regulator Guo Shuqing said in August, warning that the tally could climb even higher next year.
Regulators are also seeking to avoid a replay of the scandalous blowout four years ago in the peer-to-peer lending industry, which left depositors out of pocket by 800 billion yuan (US$121 billion) when the number of lenders shrank from more than 6,000 in 2016 to just 29.

The risk averseness also highlights the lack of financial sophistication among households in China, even as the prevalence of the internet has steepened the learning curve among the younger generation.
Regulators will look to avoid similar blowbacks from consumers by reining in the nation’s tech giants, with new proposals to regulate fintech and monopolistic behaviour, analysts said.
“The tightening of regulations governing fintech also underscores how the Chinese government and central bank’s focus has, during the second half, shifted to reducing risks from protecting growth during the first half by encouraging consumption when the country was still struggling to recover from Covid-19,” said Jefferies’ Chen.
“When the economy has found its footing, controlling retail leverage regains priority.”










