
What is net zero and how are the UK and other countries doing?
They hope to achieve the global target of "net zero" by 2050, to help slow global warming.
What does 'net zero' mean?
Net zero means not adding to the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Achieving it means reducing emissions as much as possible, and balancing out any that remain by removing an equivalent amount.
Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) are released when we burn oil, gas and coal for our homes, factories and transport. This causes global warming by trapping the sun's energy.
Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, 197 countries agreed to try to keep temperature rises "well below" 1.5C to avoid the worst impacts of climate change. Experts say that to achieve this net zero must be reached by 2050.
During COP26, nations are setting out the steps they are taking.
What has been agreed at COP26?
More than 100 world leaders promised to tackle deforestation, which contributes to climate change because trees can absorb vast amounts of CO2.
Brazil - where stretches of the Amazon rainforest have been cut down - is among the signatories, along with the UK, the US, Canada, China, Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Dozens of countries have also pledged to cut methane emissions by at least 30% by 2030. Methane is responsible for a third of current global warming caused by human activities. However, China, Russia and India have not signed up.
Chancellor Rushi Sunak is also setting out proposals to make make the UK the first "net-zero financial centre". By 2023, most big UK firms and financial institutions will have to set out detailed plans for moving to a low-carbon future.
However, commitments will not be mandatory and green groups say the proposals don't go far enough.
What other net zero action have countries promised?
Although 132 countries have publicly pledged to reach net zero emissions before 2050, China - currently the biggest producer of CO2 in the world - says it is aiming for "carbon neutrality" by 2060. It has not set out exactly what this means and how it will get there.
Russia has also pledged to reach net zero by 2060. The country is one of the world's leading oil producers, and the fourth-biggest greenhouse-gas emitter. The draft commitment hasn't been legally ratified yet.
Until recently President Putin dismissed the risks posed by rising temperatures, and US President Joe Biden criticised the Russian and Chinese leaders for not attending the COP26 summit.
India - the world's fourth biggest emitter of CO2 after China, the US and the EU - has promised to cut its emissions to net zero by 2070.
Some of the world's most heavily populated countries - including Indonesia - have not given any net zero commitment.
What else has the UK committed to do?
Presenting the net zero strategy to the House of Commons in the run up to COP26, Energy Minister Greg Hands pledged:
* £620m in grants for electric vehicles and charging points, plus £350m to help the transition from petrol
* Grants of up to £5,000 for householders to install low-carbon heat pumps
* £120m to develop small nuclear reactors (no announcement on the go-ahead for the Sizewell C nuclear power station in Suffolk)
* £625m for tree planting and peat restoration
* More money for carbon capture and storage hubs.
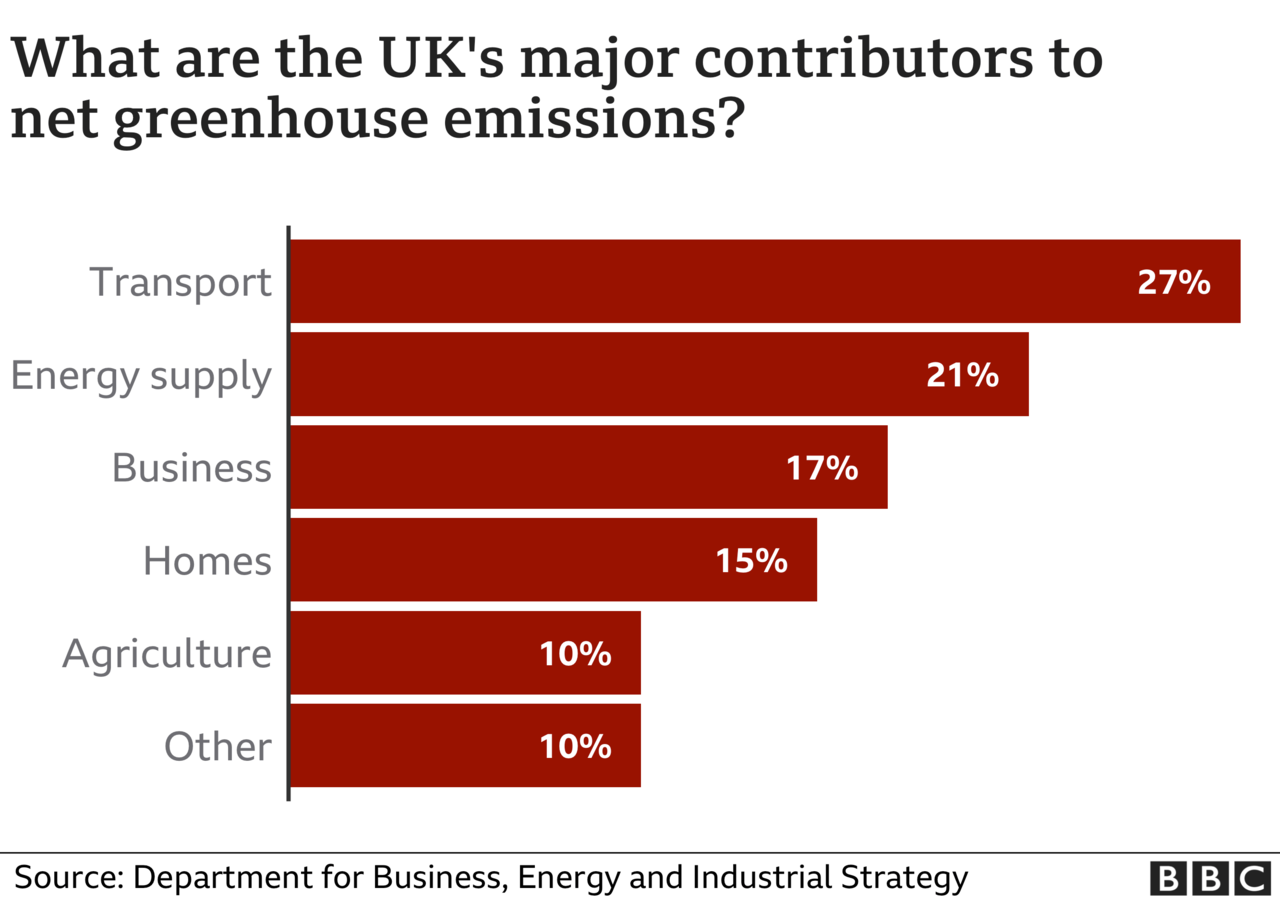
The government had already announced a ban on new petrol and diesel cars from 2030, and that all the UK's electricity will come from renewable sources by 2035.
Shadow Business Secretary Ed Miliband called the latest announcements "a massive let-down".
How else can carbon be removed from the atmosphere?
As well as tackling deforestation, almost every country is planting trees as a cheap way of absorbing carbon, although experts question whether there's enough space for the trees needed.
Technology involving carbon capture and storage has also been suggested.
This involves using machinery to remove carbon from the air, then solidifying it and burying it underground.
However, the technology is still emerging, very expensive and as yet unproven.
What are the problems with the net zero target?
There's controversy about how some countries might try to reach net zero.
For instance, Country A might record lower emissions if it shuts down energy-intensive industries such as steel production.
But if Country A then imports steel from Country B, it's effectively handed on its carbon emissions to Country B instead of reducing the sum total of greenhouse gases.
There are schemes that enable rich countries to offset their emissions by paying poorer countries to switch to cleaner fuels.
However, these are seen by some as a way to avoid taking more action domestically.
And it's hard to say that initiatives funded to offset emissions elsewhere would not have happened anyway.
The COP26 global climate summit in Glasgow in November is seen as crucial if climate change is to be brought under control. Almost 200 countries are being asked for their plans to cut emissions, and it could lead to major changes to our everyday lives.










