
What has Boris Johnson announced in his social care plan?
Boris Johnson has given the first outlines of what Downing Street is billing as a once-in-a-generation shake-up of adult social care and how it is funded, which will also help pay for a post-Covid catch-up programme for the NHS.
What has been announced?
In brief: a plan to finance adult social care through tax changes, and to modernise the social care system and ensure it is better integrated with healthcare. In the short term, much of the money being raised will finance the NHS to catch up with elective surgery and other appointments delayed due to Covid. While the financing plan is UK-wide, the actual implementation of health and social care is run by each UK nation.
How is it being paid for?
From April 2022, national insurance contributions for employees, employers and the self-employed will rise by 1.25 percentage points, and there will be the same rise in dividends tax. From April 2023, while the rises will stay the same, the tax rise will be rebranded as a health and social care levy, which will appear separately on people’s tax records.
How much will be raised and what will it be spent on?
How much is raised depends, obviously, on revenues, but Downing Street says that for the next three years the tax rise will give an additional £12bn a year for health and social care. Of this combined £36bn, £5.4bn over the three years is earmarked for social care in England, with about £500m of this earmarked for training; £16bn will be used for direct NHS England funding; £8.9bn will go on what is termed a “health-based Covid response”, seemingly the NHS England catchup; and £5.7bn will go to devolved nations, to cover both health and social care. It is not clear what proportion will be allocated to social care once the first three years are up.
What will people have to pay for their social care?
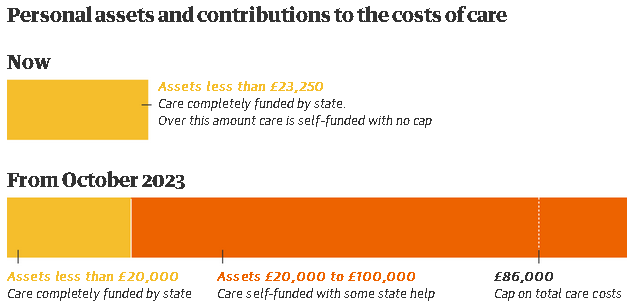
Currently in England, if people have assets worth more than £23,250, they have to pay for their social care, and there is no cap on costs, meaning some people have to sell their homes to cover these. Under the new system, anyone with assets below £20,000 will not have to pay anything from these, although they might have to make a contribution from any income.
Those with assets from £20,000 to £100,000 and above will have to contribute, on a sliding scale, although the details are set out, and it depends on contributions from local authorities, which deliver much of social care. However, people in this bracket will not contribute more than 20% of their assets each year, and once their assets are worth less than £20,000, they would pay nothing more, although they might still contribute from any income.
Those with assets above £100,000 must meet all fees until their assets fall below £100,000. There is a maximum payment towards care of £86,000, which ministers say is about the equivalent of three years of full-time care.

This new means test system comes into force in October 2023 – until that point some people will still have to pay more than £86,000 in total.
What other changes are planned for social care?
Beyond the promise to bring the health and social care systems together, there is little detail so far on the overhaul of social care, beyond the prospect of a white paper to develop longer-term plans. The current plan does pledge £500m over three years for social care workforce training and recruitment, and extra money set aside to local authorities to help deliver social care, and to deliver the integration, though without any specific sums for these.
Is this a UK-wide system?
National insurance is a UK-wide system, although rates and thresholds can differ. The income from the new levy will be distributed across the four UK nations. The government says that by 2024-25, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland will benefit from an extra £1.1bn, £700m and £400m respectively. However, health and social care are devolved and differ significantly, meaning issues such as the cap and floor for people’s personal outgoings on care will also vary.
How much will the higher NI rates cost people?
According to Downing Street figures, someone earning £24,100 a year would pay an extra £180 a year. A person on £67,100 would pay £715 more. Those earning less than £9,500 a year, the threshold for national insurance, will still pay nothing. Although people above the state pension age who still work do not normally pay national insurance, once the rise is rebranded as a health and social care levy from 2023, they will pay this.
Why is the NHS getting so much of the money?
Because, Downing Street says, routine NHS work has been so badly hit by Covid, with a waiting list in England for elective treatments of 5.5 million people, which ministers say could reach 13 million by the end of the year. The extra money is intended to fund 9m more appointments, operations and treatments.
Will the money ever be moved from the NHS to social care?
Time will tell. Downing Street insists that after the coming few years the exceptional demands on the NHS will reduce, and there will be more money free for social care. However, NHS budgetary demands have rarely, if ever, gone down in the past, and this could prove quite a political challenge.
Does this solve the social care crisis?
No – this is just a first step on how a plan may be financed, with almost all details of how care and health can be better integrated still to be worked out. And while the government’s 32-page plan pledges that councils will have access to sufficient funds to meet their social care demands, local authorities have long complained that they are left short.











