
The co-founder of BioNTech designed the coronavirus vaccine it made with Pfizer in just a few hours over a single day
The Food and Drug Administration granted emergency authorization to Pfizer and BioNTech's coronavirus vaccine on Friday.
The two-dose vaccine is the first to be authorized in the US, though Moderna's coronavirus vaccine will likely receive FDA authorization this month as well.
After months of testing, the vaccine was found to be 95% effective in preventing COVID-19 in a large-scale trial. Its development process was unprecedentedly fast — no other vaccine in history has been created and manufactured so quickly. Previously, the fastest vaccine ever developed took more than four years.
But perhaps most remarkably, BioNTech co-founder Ugur Sahin designed the vaccine in just a few hours in mid-January, according to The Journal, a podcast from Gimlet and The Wall Street Journal.
A BioNTech spokesperson confirmed to Business Insider that Sahin — who founded the company with his wife, Özlem Türeci — made a "rough design over one weekend."
Moderna's vaccine also took just two days to design, as Business Insider previously reported. The reason both candidates could be designed so quickly comes down to the technology they rely on: messenger RNA, or mRNA.
The FDA had never approved an mRNA-based vaccine or treatment before. But now that the agency has granted authorization to Pfizer and BioNTech — with Moderna's likely to follow shortly — mRNA vaccines could set a new industry standard.
How mRNA vaccines train the body to fight the coronavirus
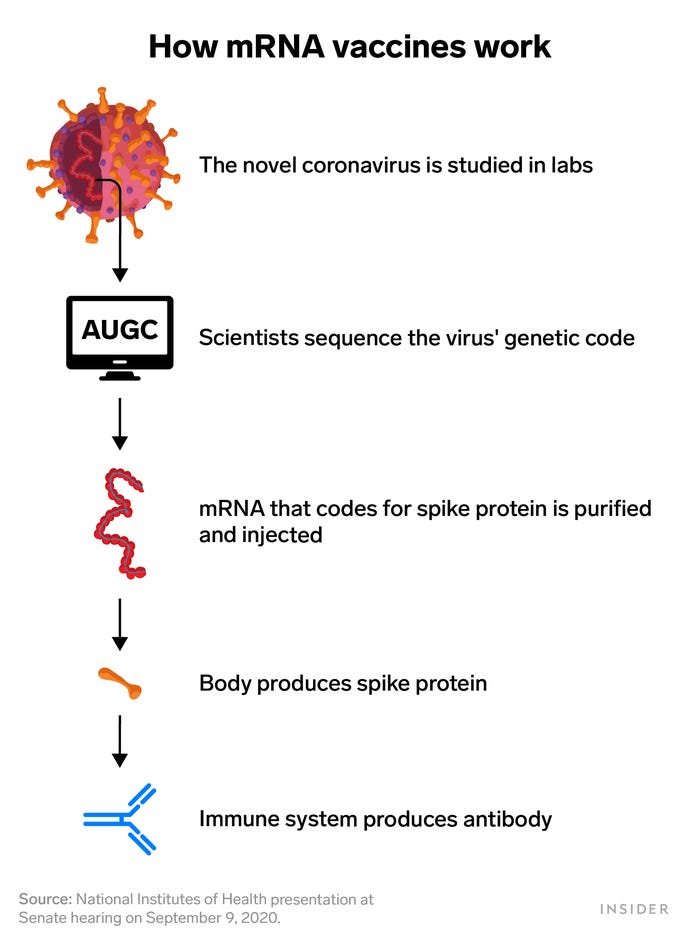
Messenger RNA is genetic material that tells cells how to make proteins. Pfizer's coronavirus vaccine candidate works by injecting a small piece of coronavirus mRNA into the body. That RNA codes for the virus' spike protein, which is what helps it attach to and invade cells. That's also what antibodies target and neutralize.
So the mRNA vaccine spurs the body to produce the spike protein internally in order to trigger that same immune response.
Moderna's candidate works in the same way and has been found to be 94.5% effective in trials.
Utilizing mRNA vaccine technology meant BioNTech and Moderna only needed the coronavirus' genetic sequence to design a vaccine. That's why they could move forward so quickly.
How BioNTech and Pfizer joined forces

On January 24, Sahin read a paper in The Lancet that described Chinese family members who traveled to Wuhan then contracted COVID-19.
"What was most concerning is that one of the family members had the virus and was virus-positive but did not have symptoms," Sahin told The Journal. This meant that the virus could be transmitted by asymptomatic carriers — and had probably already spread out of China.
"The math behind it just showed me it will happen, it's just a matter of a few weeks," Sahin said.
He decided to shift BioNTech's focus toward a coronavirus vaccine. The following week, Sahin told the company that operations going forward would be devoted mostly to developing and testing the vaccine.
Using the coronavirus' genetic sequence, which Chinese researchers published on January 11, Sahin designed 10 different candidates on his computer that weekend. One was the candidate later selected for larger trials — the one the FDA has authorized.
Sahin designed that winning candidate in just a few hours, according to The Journal.
But BioNTech, with a pre-pandemic workforce of 1,000, didn't have the capacity to manufacture the hundreds of thousands of doses needed for large-scale trials — let alone the hundreds of millions it would need if the vaccine worked.
So in February, Sahin called Pfizer's head of vaccine research, Kathrin Jansen; BioNTech had worked with Pfizer since 2018 on a flu vaccine.
"This is a disaster, and it's getting worse," Dr. Jansen told Dr. Sahin, according to The Wall Street Journal. "Happy to work with you."
The two companies announced their partnership in mid-March.

Pfizer would manage the logistics, including manufacturing the vaccine in large batches and organizing the Phase 3 trial, which wound up involving 43,500 volunteers. BioNTech, meanwhile, handled the vaccine's design.
Pfizer and BioNTech announced that their vaccine was more than 90% effective on November 9. When Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla told told senior company officials of the findings, people jumped up from their chairs, The Wall Street Journal reported.
The full results of the Phase 3 trial were even stronger: The findings, published in the New England Journal of Medicine on Thursday, suggest that the vaccine doesn't trigger severe side effects in most people and is 95% effective at preventing COVID-19.
Anthony Fauci, the nation's leading infectious-disease expert, called the results "just extraordinary" and said they would "have a major impact on everything that we do with regard to COVID."
The speed at which BioNTech and Pizer developed the vaccine does not mean they sacrificed thoroughness, according to Albert Rizzo, chief medical officer for the American Lung Association.
"We're not skipping steps — we actually have better technology," Rizzo previously told Business Insider. "Why did it take two weeks to cross the Atlantic back in the 1800s? Well, we had to go on a boat. Whereas now, you can get across the ocean in several hours."
The pros and cons of mRNA vaccines
For decades, vaccines contained a dead or weakened version of a virus itself. Then early advances in genetics allowed vaccines to use proteins made by the virus instead. That method was first used in the 1980s to develop a vaccine for hepatitis B. Companies like Novavax are relying on the same protein-based model to create their coronavirus vaccine candidates.
But BioNTech was founded on the idea that mRNA could be used to develop cancer vaccines, hence its mRNA-based approach to the coronavirus. One of the company's senior vice presidents, biochemist Katalin Karikó, first discovered how to configure mRNA to be used in vaccines.
Since RNA vaccines aren't cultivated using cells, they're quicker to produce.
The drawbacks of Pfizer and BioNTech's vaccine, however, are that people must get two injections three weeks apart, and it needs to be shipped at about -94 degrees Fahrenheit. That requires dry ice and special freezers.
Crucial questions about the vaccine also remain, like how long it will protect people from COVID-19 and whether it can prevent transmission and asymptomatic infection.










