
Why the world is still arguing over face masks, 20 months into the pandemic
Spikes in transmission were met with lockdowns; international travel was heavily restricted; and though domestic constraints frequently proved controversial, hygiene measures like social distancing, hand-washing and mask-wearing were strongly encouraged -- if not legally mandated.
But those days are behind us. Pandemic management now differs widely from country to country -- with the face mask just one example of the world's increasingly fractured approach to Covid-19.
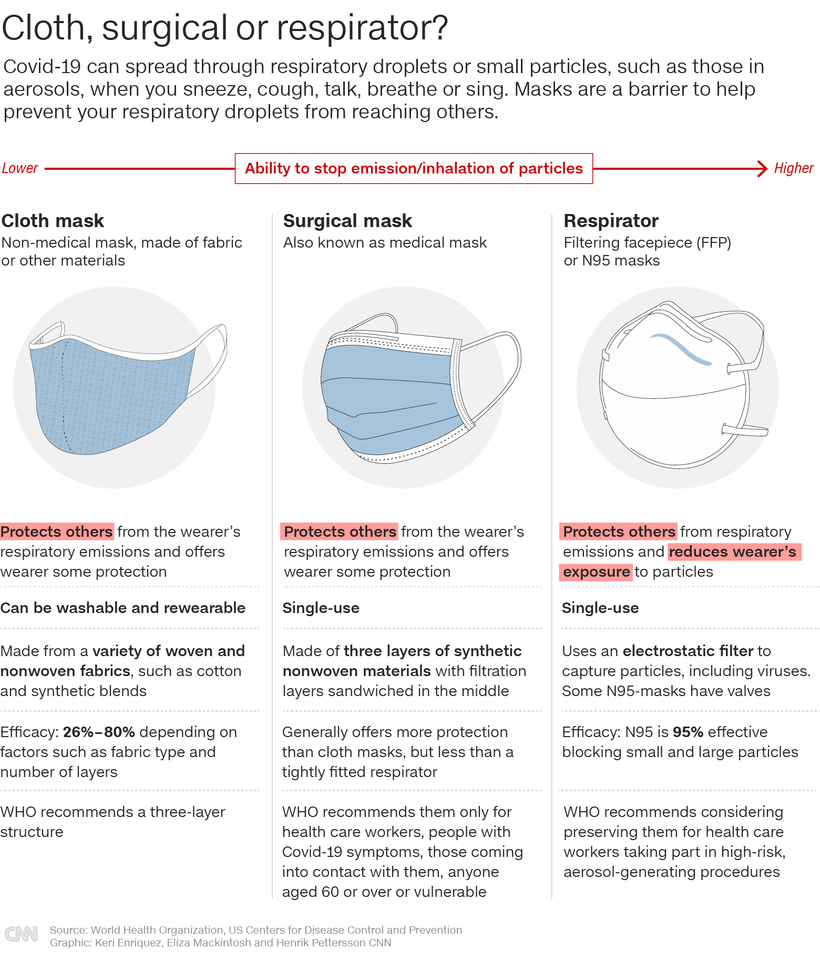
The science behind masks is fairly clear, and has only become more robust over the course of the pandemic. Studies have shown that masks significantly decrease the chances of transmitting coronavirus, and some types of masks can help prevent their wearers from catching the virus.
Yet debates still rage in multiple countries over their use, and some regions have recently removed mandates that people wear them in crowded spaces.
"Masks remain a symbol of a divided society -- between those who feel we have restricted too much and those who feel we have not intervened enough during the pandemic," Simon Williams, a senior lecturer on Covid-19 behaviors at Swansea University in Wales, told CNN.
With the prospect of another winter pandemic brewing, some countries are grappling with calls to return to mask use. But they face resistance from people fatigued by endless mixed messaging -- and many experts fear that in countries where rules have been relaxed, reimposing mandates could be complicated.
Different approaches
The first days of the pandemic saw early hesitance over the use of face masks from governments and the World Health Organization (WHO), amid fears that a rush for masks would leave frontline workers without enough protective equipment. But that as the world learned more about Covid-19, their use became commonplace by the middle of 2020.
"Masks help to filter out aerosol that is generated in our respiratory tract when we breathe or speak. (They) are most effective at filtering out larger aerosol particles and less effective at filtering out the smallest ones," said Bryan Bzdek, research fellow at the University of Bristol's Aerosol Research Centre, summarizing the scientific mechanism behind mask use.
"This is conceptually similar to driving a car when there are a lot of insects about -- the large ones tend to impact against the windshield whereas the small ones follow the air flow around the car," he said.
Outside parts of south-east Asia, where mask-wearing had become common after the SARS outbreak in 2002, few countries were used to covering their faces in public. But the unique shock of the Covid-19 outbreak meant behaviors quickly changed, experts say.
"Behavioral scientists and policymakers were quite surprised at how quickly people adopted masks once they were required," WIlliams said.
"The biggest development in mask perceptions over the pandemic has been an acceptance generally that they protect others as much, if not more, than the wearer," he added.
"The exact benefits in terms of cases prevented and lives saved are still being studied -- but even marginal gains are worthwhile when masks are relatively low-cost interventions, in that they are much easier for us than things like distancing or isolating."
But now, despite the body of scientific research into face masks only expanding, countries are heading in various directions.
In the US, President Joe Biden has made masks a key pillar of his Covid-19 response. His administration has followed guidance from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on mask recommendations, imposing them on federal property and encouraging schools to use them.
But he's faced obstacles from several states. Most recently, Biden's Department of Education has become embroiled in a battle with Florida's Education Department after it decided to reduce funding for certain school districts for requiring people wear masks.

In Europe, mask mandates have become the norm even as several countries saw their Covid-19 cases and hospitalizations come under control, with stricter rules for unvaccinated people attending indoor spaces like restaurants and bars.
Spain, for instance, requires masks indoors when social distancing is not possible. France recently lifted its requirement to wear a mask outdoors, but the rule remains in place for enclosed spaces. And Italians are still required to cover their faces inside or on public transport (the outdoor mask mandate has now been lifted).
However, England, in spite of a stubborn surge in cases since the summer, no longer requires people to cover their faces anywhere -- with British Prime Minister Boris Johnson leaving it up to "personal choice."
The psychology behind masks
Experts say that whether most people will wear masks depends largely on the rules that are in place.
"The single biggest influence across all reason of face mask wearing appears to be the law," said Ivo Vlaev, a professor of behavioral science at the University of Warwick. He cited data from Imperial College London's Covid Behaviour Tracker, the largest rolling study of the societal impact of Covid-19 in the world.
 A metro train in Italy, where mask wearing is required in most indoor spaces.
A metro train in Italy, where mask wearing is required in most indoor spaces.
"(Mandating) a behavior helps send out the signal that it is important," Williams added. "Mask wearing is a behavior that is really influenced by social norms -- or peer pressure -- and so in a setting where masks are no longer mandated, this might influence others not to wear theirs."
"This is well illustrated by the inflection point in the UK when compulsory mask wearing was announced," Vlaev said, noting a quick pick-up in mask use last year, and an equally sudden drop since July when the rule was removed. According to the Office for National Statistics, nearly one in five Brits no longer say they wear a face covering outside their home, compared to just 4% in mid-June when they were still mandated.
But when the public takes their cues from the law, unclear messaging can be costly.
Williams said he was initially "surprised" by how quickly people stopped wearing masks in the UK in recent months. "It is really down to the mixed messages that many people feel government have been passing on," he added.
"Many countries in Europe have had a more consistent policy on masks and so this makes it become more of a habit over time."
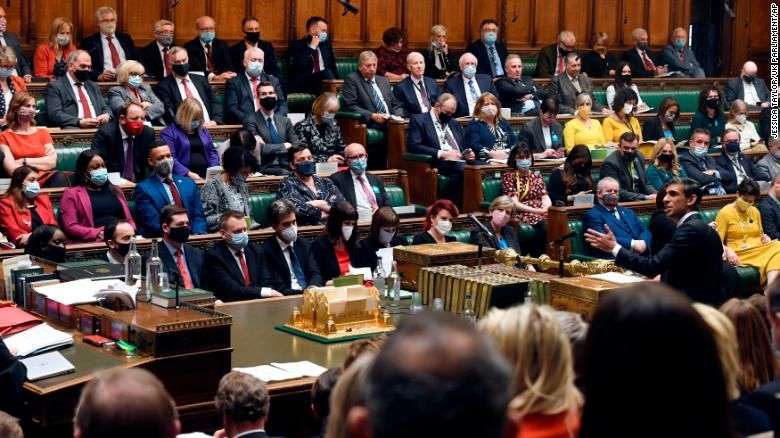 Britain's lawmakers wore masks in the House of Commons last week, after
the health secretary encouraged them to 'play their part' in curbing
Covid-19 transmission. Few MPs were spotted in face coverings before
last week.
Britain's lawmakers wore masks in the House of Commons last week, after
the health secretary encouraged them to 'play their part' in curbing
Covid-19 transmission. Few MPs were spotted in face coverings before
last week.
Britain's government now faces a test as it attempts to encourage mask-wearing again, without the backing of a law, as cases rise in the run-up to winter.
The UK's health secretary, Sajid Javid, recently urged people to wear masks in certain situations to avoid future restrictions. But he was forced to admit it was "fair" of the public to wonder why they are now being encouraged to do so, when lawmakers had hours earlier appeared in the House of Commons without face coverings.
Experts doubt whether such guidance will carry as much weight as it did during previous stages of the pandemic.
"As the number of mask wearers falls off, the ability of authorities to enforce mask mandates falls away," said Robert Dingwall, a professor of social sciences at Nottingham Trent University.
It's that thinking that has led most EU countries to impose longer, and occasionally stricter, mask measures.
"People will have learned a new behavior -- wearing masks -- before 'unlearning it', and then having to re-learn it," Williams said. "This could prove challenging -- many people may have gotten used to life without masks."










