Unpacking the white paper on ‘Hong Kong democracy’
More than a week before Hong Kong’s Legislative Council election under a Beijing-imposed overhaul was held on December 19, the State Council’s white paper on the city’s democratic development was completed and ready to be released at any time. The “publish” button was pressed 11 seconds past 10am the following day.
The official document, titled “Hong Kong Democratic Progress Under the Framework of One Country, Two Systems”, saw the light of day nine minutes before all election results were announced on December 20.
Mainland experts familiar with the central government’s thinking on Hong Kong affairs have noted that the publication of the official document and the ensuing high-profile publicity campaign to attack Western-style democracy is part of Beijing’s coherent strategy to capture what it sees as the moral high ground on Hong Kong’s democracy.
“It is part of Beijing’s grand strategy of governing Hong Kong in the new era, which highlights the need for theoretical justification on top of practice,” a mainland academic familiar with the drafting stage of the white paper told the Post.
 In the days that followed the release of the white paper, officials and
experts appeared in media briefings as part of an extensive publicity
campaign.
In the days that followed the release of the white paper, officials and
experts appeared in media briefings as part of an extensive publicity
campaign.
Seasoned analysts said the document should be read in parallel with another white paper called “China: Democracy that Works”, also released by the State Council Information Office three weeks ago as part of a broader effort to promote the country’s system of governance as more effective than the model exemplified by the United States.
The timing of the first white paper was not coincidental, they said, coming just days before the US convened a “democracy summit” of friendly countries, an event seen by critics as an attempt to forge an alliance against China and Russia.
Seen together, the white papers were a consequence of the larger geopolitical tensions between China and the US, with Hong Kong caught up in it as a high-stakes ideological battleground, analysts said.
Tian Feilong, an associate professor at Beihang University’s law school who advises Beijing on Hong Kong affairs, said the Hong Kong white paper was not an “isolated document” but a carefully crafted move by the central government.
“It is a sequel to the white paper on China’s democracy,” he said.
“The white paper devotes a lot of coverage to the importance of promoting diversified forms of democracy in Hong Kong, a core message highlighted in the document on China’s democracy,” he said.
 Lawmakers-elect for Hong Kong pose for a picture. The white paper was issued by Beijing the day after the legislative poll.
Lawmakers-elect for Hong Kong pose for a picture. The white paper was issued by Beijing the day after the legislative poll.
The white paper on Hong Kong’s democratic development stressed that democracy cannot be reduced to the “simplistic question of whether there are elections, and elections themselves cannot be defined exclusively as direct elections”.
“What matters is whether public representation is expanding and whether the fundamental interests and the common will of the people are faithfully represented. For democracy to develop in Hong Kong, measures should be taken to improve the electoral system, and more forms of democracy – consultation, inquiry, hearing and dialogue – should be tested, to open up more channels for democracy of quality and substance,” the document read.
Tian said he expected the central government to stress in the coming months the importance of delivering “substantive democracy” in Hong Kong. “Instead of the degree of competition in elections, good governance, the quality of those returned in elections and the performance of the government in resolving livelihood issues will become the major yardsticks of success or failure of democracy in Hong Kong,” he said.
Tian said, based on the experience of the central government’s drafting of crucial official documents, it usually took a long time to prepare and pen such a white paper, involving multiple rounds of consultations among experts.
The document, the second such white paper on Hong Kong affairs since 2014, highlighted China’s determination to develop democracy with “Hong Kong characteristics”. It also renewed the central government’s pledge to pursue the ultimate goal of electing the city’s leader and legislature by universal suffrage, as set out in the Basic Law.
It came as a surprise to critics who had questioned Beijing’s commitment to such a goal after the 2019 anti-government protests and the ensuing political shake-up.
However, a mainland expert familiar with the drafting process of the white paper said the central government would not avoid the issue of universal suffrage. “But Hongkongers should no longer look at the issue from a linear perspective, assuming that the number of directly elected seats must increase as time goes by,” the source added on the condition of anonymity.
The white paper laid out a detailed argument that there was no democracy in Hong Kong under British colonial rule, and that it was only the city’s return to Chinese sovereignty in 1997 that “ushered in a new era for democracy”.
“Britain exercised a typical colonial rule over Hong Kong … but [it] rushed through electoral reform in Hong Kong in the very short remaining period of the colonial rule,” it said.
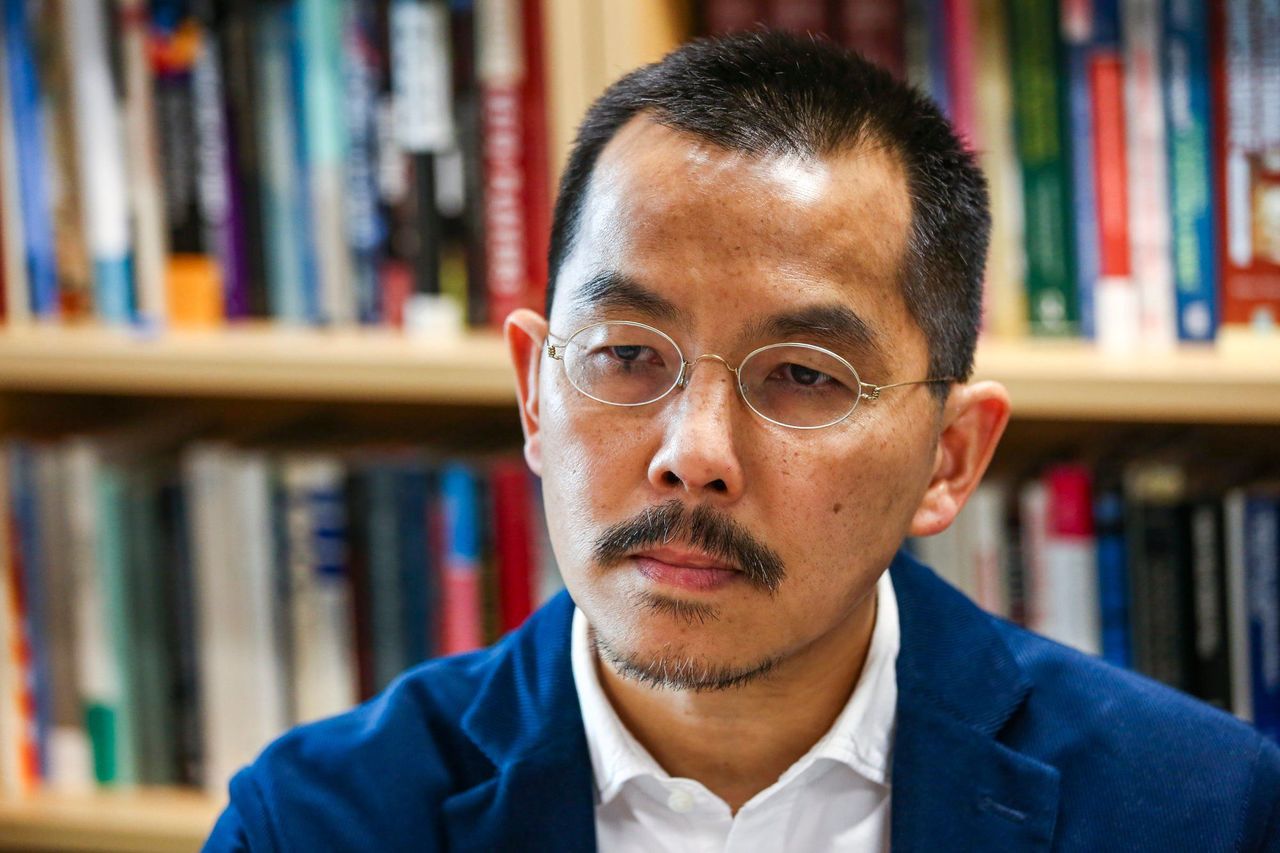 Ray Yep, City University political scientist.
Ray Yep, City University political scientist.
Ray Yep Kin-man, a political scientist at City University, said: “All governments need a narrative to convince their own people and foreign countries on controversial issues. China is no exception.”
He said Beijing intended to appeal to the international community and mainlanders for support on its stance on democratic development in Hong Kong.
“However, Beijing’s narrative on the history of democratic development in Hong Kong was quite different from the understanding of many Hong Kong people,” Yep said.
Yep, who has been studying Hong Kong’s history using declassified British files in the past decade, said according to declassified UK archives, the British government said it decided not to press ahead with democratic reform in Hong Kong after the second world war and the 1950s because of Beijing’s opposition.
In 1946, the post-war governor, Sir Mark Young, announced his plan to usher in an age of direct elections and “a municipal council constituted on a fully representational basis”.
Young retired in 1947, and left his “Young Plan” in the hands of his successor, Sir Alexander Grantham. But the idea never got off the ground as Grantham did not think Hong Kong needed elections and businesses could continue their ways with the British acting as benevolent dictators.
On how the white paper did not mention Beijing’s reservation about democratic reforms for Hong Kong after the second world war as cited in the British documents, Professor Anthony Cheung Bing-leung, former transport and housing minister, pointed to a disadvantage China faced.
Cheung, a political scientist by profession, noted that the British government had an established practice of releasing official archives regularly.
“But there is no such arrangement under mainland’s mechanism. Instead, Beijing relies on publishing memoirs of retired officials handling Hong Kong affairs, without a systematic or transparent mechanism to release archives,” Cheung said. “It means Beijing would be in a disadvantageous position in the debate on history of democratic development in Hong Kong.”
This and other mini-debates surrounding the white paper were likely to continue for awhile, analysts noted.