
UK scientists set new record for generating energy from nuclear fusion with reaction '10 times hotter than the sun'
Scientists in the UK have set a new record for generating energy from nuclear fusion, the same process that powers our sun seen as a potential future source of near limitless power.
The Joint European Torus, or JET, an experimental fusion machine near Abingdon in Oxfordshire, generated around 59 megajoules, or 11 Megawatts of energy - enough to power around 10,000 homes - in a five second burst.
The experiment still consumed more energy to create the fusion reaction than the energy released by it, but a sustained fusion event of this kind is a major advance.
"These landmark results have taken us a huge step closer to conquering one of the biggest scientific and engineering challenges of them all," said Professor Ian Chapman, chief executive of the UK Atomic Energy Agency that co-funds and operates JET.
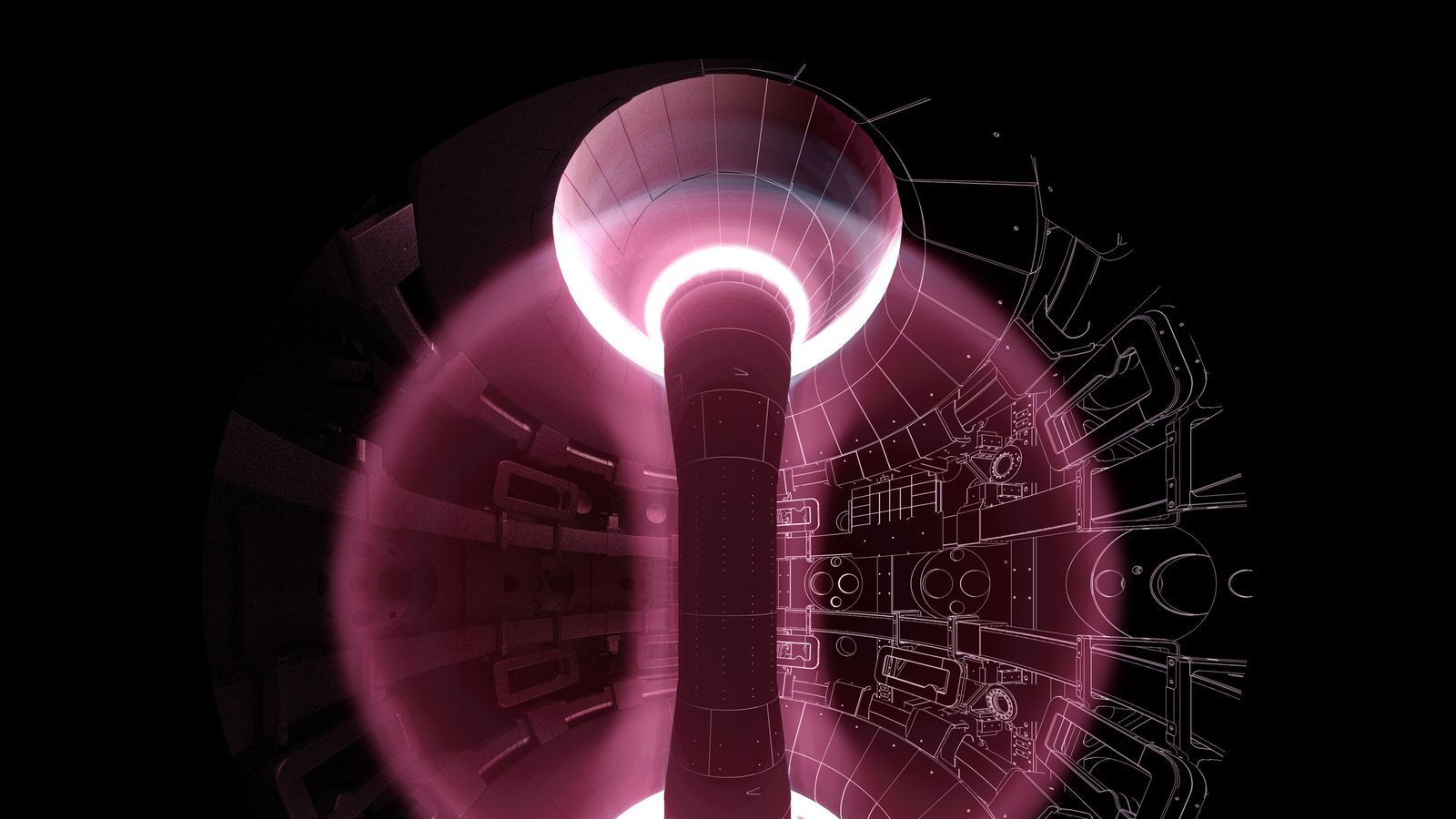
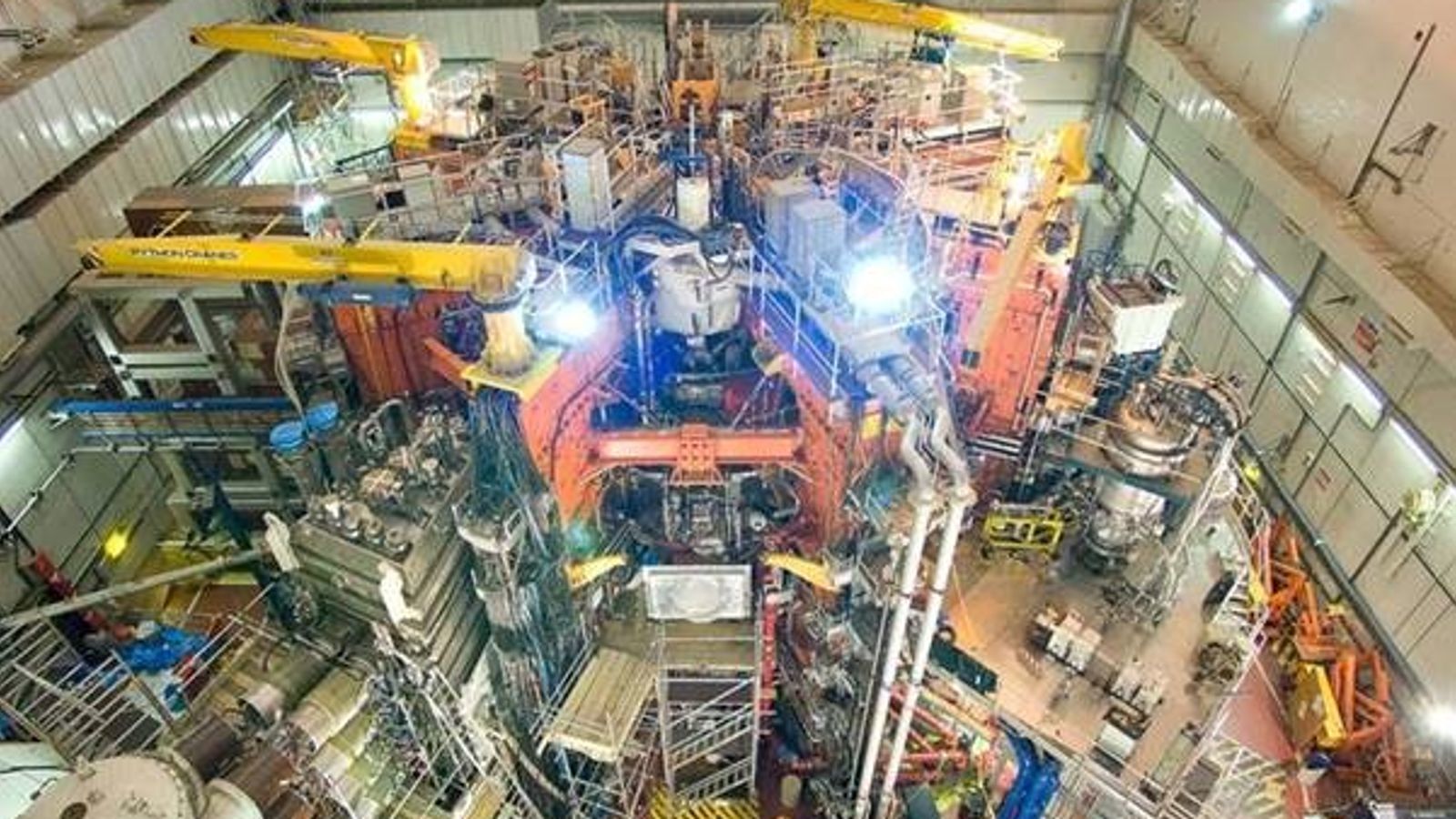 The Joint European Torus uses a hollow doughnut-shaped reactor vessel called a Tokamak to heat its fusion fuel
The Joint European Torus uses a hollow doughnut-shaped reactor vessel called a Tokamak to heat its fusion fuelWhat is the difference between nuclear fission and fusion?
Unlike nuclear fission, which powers conventional nuclear reactors by splitting radioactive elements to release energy, fusion does the opposite.
It forces two forms of hydrogen to fuse together releasing around four times more energy by weight of fuel than a nuclear fission reactor and four million times more than burning fossil fuels.
But containing the same reactions that power our sun here on Earth is the tricky part.
JET uses a hollow doughnut shaped reactor vessel called a tokamak to heat its fusion fuel - "heavy" hydrogen atoms deuterium and tritium - to 150 million degrees Centigrade.
This forms something called a plasma that's around 10 times hotter than the sun - making the reactor, for the few seconds it is running, the hottest place in our solar system.
Electromagnets surrounding the tokamak prevent this charged soup of ions from touching the sides and the whole reaction stopping.
Holding the plasma in this way allows fusion to occur, releasing energy. The latest results from JET prove that making fusion energy in this way is at least theoretically feasible.
'Landmark' advance in fusion technology
"59 Megajoules of heat energy from fusion over a period of five seconds is a landmark in fusion research," said Professor Ian Fells from the University of Newcastle.
But the possibility of commercial fusion energy is still open to debate.
Since the 1950s there have been many incremental steps forward toward fusion power. But the dream of a commercial nuclear fusion reactor has never even been close to being realised.
Could these results change that?
"They give confidence that the prize of fusion energy is worth pursuing," said Professor Sue Ions, nuclear engineer and fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering.
 In May 20201, the UK
Atomic Energy Authority's MAST Upgrade experiment developed an exhaust
system that can deal with the immense temperatures
In May 20201, the UK
Atomic Energy Authority's MAST Upgrade experiment developed an exhaust
system that can deal with the immense temperatures
It's a major boost for the €20bn (£16.9bn) International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) which is under construction in the south of France.
The project is a collaboration between the world's major economies to build a scaled-up version of the JET experiment.
It's seen as the full "reactor-scale" demonstration of the technology that engineers would require to learn how to build a commercial reactor.
Doubts of fusion's commercial viability
But ITER is not the only game in town. Last year the US National Ignition Facility (NIF), at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California succeeded in creating fusion by a different method of compressing a plasma using immensely powerful lasers.
And in the decades since large government-backed projects like JET, NIF and ITER were conceived small, private fusion ventures have been springing up.
Super-rich investors like Jeff Bezos and venture capitalists keen to back the next revolution in low-carbon energy have led to a profusion of small fusion projects, some using laser-based methods, others using miniaturised versions of the JET and ITER machines.
But few have achieved fusion, let alone "break even" the point where more energy comes out of the reactor than has to go in to get fusion started.
Few think fusion could arrive before 2050 - time to address the climate crisis. Some doubt it will ever happen.
The Tokamak reactor design was first proposed by Russian scientists in 1950. The joke in nuclear fusion circles is that a working reactor has been 20 years away ever since then.
But today's advance might mean fusion scientists have the last laugh.










