
Deepfakes, widely used for fake nudes, could disrupt financial markets
Experts have been sounding the alarm about weak biometric data security for years. The problem has looked especially pernicious in China, where facial recognition is now a ubiquitous form of identification. Now the rise of deepfakes could be creating new problems, experts say.
Despite widespread concern about technology, which allows a person’s likeness to be imitated through audio and video, there are few real-world examples of hackers successfully exploiting it for monetary gain.
One of the big concerns has been the idea that deepfakes – to date mainly known for their use in celebrity nudes – could be used to trick facial recognition systems. So far, there is little evidence that this is something that scammers could easily pull off. But some are concerned about other potential problems related to deepfakes that go beyond just personal security to possibly eroding trust in the institutions that handle our money.
“There is an additional problem that deepfakes create,” said Jon Bateman, a fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace who researches cybersecurity in the financial sector. “That’s not the threat of deception, but the threat of distrust and cynicism, where people start to automatically assume things are fake, because it’s possible to create a deepfake.”
While Bateman said it is extremely unlikely that a deepfake could cause a market crash in an advanced economy with mature financial markets, sowing distrust comes with other pitfalls.
It could, for example, contribute to existing anxieties in a financial crisis, especially in less developed countries that already have a high level of distrust, he said. If consumers start to worry about the security of their bank accounts, it could cause a bank run.
Many people working in cybersecurity are also thinking about these problems. In a survey of 105 chief security officers published by biometric authentication provider iProov in January, 77 per cent said they were concerned about the potential impact of deepfake video, audio and images.
The most cited threat was the fraudulent authorisation of payments and transfers, according to the survey published by biometric authentication provider iProov.
While real threats may be rare, it is not purely theoretical. In one unusual case last year, fraudsters used artificial intelligence-based software to fool the CEO of a UK-based energy firm over the phone.
The CEO thought he was talking to the head of his German parent company and wound up sending €220,000 (US$242,000) to what he thought was a supplier. The deepfake audio impersonated the boss’s voice down to his slight German accent.
PwC partner Kok Tin Gan said threats posed by the technology are to be expected.
“Whenever there’s a new technology in place that’s commonly used, that creates an opportunity for the hackers to take advantage because that’s where they can earn money,” said Gan, who calls himself a hacker by profession.
Some companies are already moving to reassure people that deepfakes do not present a problem for their systems.
After a face-swapping app called Zao went viral on Chinese social media in 2019, mobile payments platform Alipay sought to allay fears about the technology. “There are currently many types of face-swapping programs online, but no matter how lifelike the results are, it is impossible to break through facial recognition payments,” the company posted on Weibo.

Alipay is one of China’s most widely used mobile payment apps and owned by Ant Group, an affiliate of South China Morning Post parent company Alibaba. Because of widespread appeal, it has been targeted by hackers.
In a 2018 crime that eventually saw five people arrested in China, a group used leaked personal data and photographs to try to steal money through Alipay.
The personal information was used to register accounts on Alipay and the photos were used to create 3D avatars in an attempt to fool the facial recognition. But the logins were quickly flagged and the plan failed.
Facial recognition is now widely used in China, where the technology can be found in everything from banking apps to toilet paper dispensers. But several data leaks in recent years have raised concerns and prompted some backlash.
Large caches of images have shown up online alongside phone and national ID numbers. In one particular case, a bundle of 5,000 images of faces was selling online for just 10 yuan (US$1.40).
Gan said he thinks deepfakes should make people think more about the consequences of giving out their biometric data. While there are advantages to using biometric data for authentication, people cannot change faces or fingerprints the way they can a compromised password, he said.
But as with any new technology, new forms of cyberattacks are being met with new defences. One way companies protect their users is through multiple methods of verification.
If you scan your face to access a banking app, for example, this will only cover the initial authentication, Kok said. Access to other services may still require the familiar tokens and codes sent via SMS. Banks also typically have transfer limits.
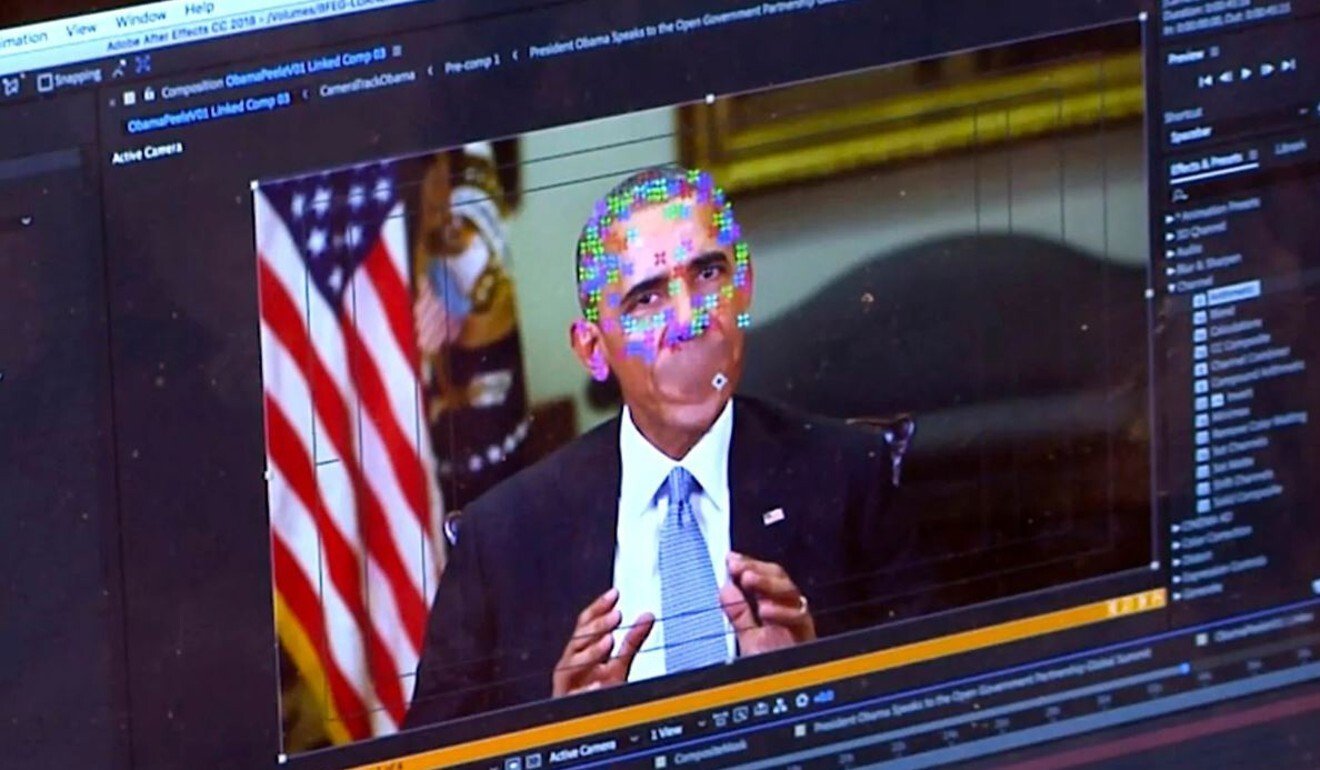
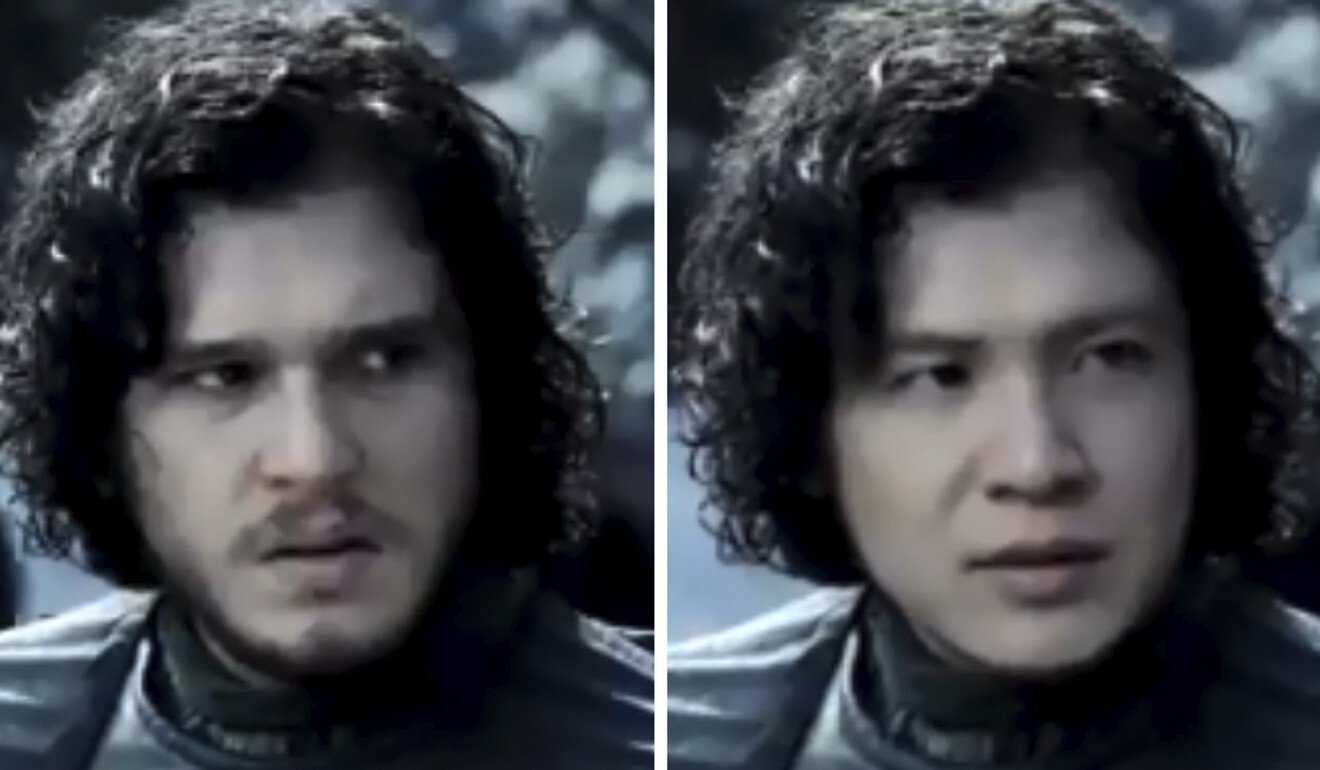
Until recent scares over facial recognition, deepfake scams were more commonly associated with fake nude photos or videos shared online. Deepfake pornography that spliced celebrities into adult videos became a widely publicised issue in China last year.
The technology has also been used for more humorous purposes. In October, South Park creators Trey Parker and Matt Stone unveiled a new deepfake show called Sassy Justice on YouTube. The show featured the likeness of US President Donald Trump and Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg, among others.
While Kok said he recognises that deepfakes tend to be used more for pornography now than anything else, he said stronger legislation and more transparency from companies will be needed to counter new problems from deepfakes and biometric data breaches.
“I’m sure there will be one massive incident that will cause disruption,” he said.
Some regulators and central banks are also growing concerned about the potential for deepfakes to disrupt markets. Some fintech groups and banks, including HSBC, have already started to prepare for the threat, the Financial Times reported in September.
The potential threats come in different forms: fraudulent accounts could be created for money-laundering; accounts belonging to high-profile individuals could be hijacked; or businesses could be tricked into sending funds to scammers.
For now, experts are still divided on whether deepfakes pose a significant threat. Bateman, the cybersecurity researcher, said that deepfakes are just one among many threats targeting payment apps and financial institutions.
While some believe that deepfakes just give old bank fraud scams a new form, other experts believe that they could lead to an entirely new level of distrust and require new technologies and practices to counter them, Bateman said. Financial institutions are aware of the threat, but there is no consensus on how much it should be prioritised.
“What we’re seeing is the first wave of efforts by the financial sector to experiment with counter technology,” Bateman said. “And I think that’s appropriate because this is an emerging threat. It’s not yet an all-hands-on-deck moment.”
Some researchers and tech companies are already working on solutions such as detection algorithms that can spot sophisticated fakes. This includes Microsoft, which recently developed a video authentication tool that tries to detect signs that an image has been artificially generated in ways that might be invisible to the human eye.
In China, public attitudes about biometric data are already changing. In a survey of more than 6,000 people in 2019, more than 80 per cent said they fear facial data leaks, and 65 per cent were worried about deepfakes. As with other technologies, though, it may take years before the public becomes broadly aware of the problem.
As Gan pointed out, it took more than a decade for people to become aware of the problems brought by social media platforms. Once seen a boon to people looking to stay connected to friends and family, social media is now widely criticized over concerns about user privacy and misinformation.











