
What the latest vaccine news means for lifting lockdown
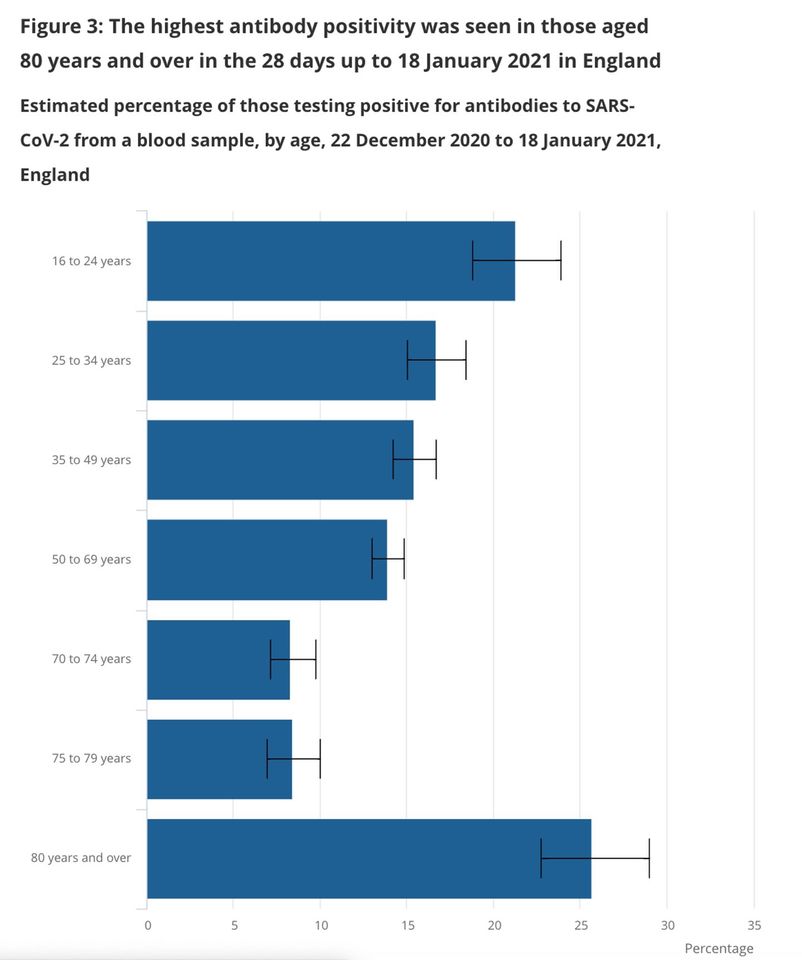
Today’s antibody survey from the Office for National Statistics shows 15.3 per cent prevalence in England, up from 10.7 per cent last month. This time around, the increase is not just due to infections: vaccines are playing their part too. The highest antibody positivity is seen in the over-eighties, who have been prioritised for vaccination. While the latest survey will only reflect the first few weeks of the vaccine rollout (it takes several weeks to build up antibodies), it suggests the next survey may show some extraordinary figures, as millions of jabs start to show their results.
Meanwhile, yesterday’s publication of Oxford University’s pre-print paper on the efficacy of the vaccine provided a significant optimism boost: one jab is estimated to have 76 per cent efficacy for preventing symptomatic infection (6 percentage points higher than the original estimate published for two doses last year). Ross Clark has the details of the trial on Coffee House, which recorded zero hospitalisations for those who received the vaccine. Crucially, the study also found the jab cut transmission of the virus by 67 per cent.
That figure is perhaps even more important than the upward revision of efficacy: it means that the vaccine doesn’t simply protect the person receiving it from severe Covid-19 symptoms, but it also stops two-thirds of people from passing the virus on. This would suggest that even with only the most vulnerable groups eligible for vaccination at the moment, inoculation will significantly reduce the spread of Covid-19. The thought has ministers and officials thrilled: similar to hopes around efficacy, the success of these vaccines is surpassing all expectations.
The extent to which vaccines reduce transmissions is a key factor in how quickly the UK can reopen. Concerns over young people still catching the virus (roughly 65 per cent of Covid-19 positive patients admitted to intensive care are currently under 65) will diminish as the virus struggles to circulate through millions of vaccinated people. Those who did catch it would be easier to care for, with demands on hospital capacity bound to ease as the elderly and vulnerable are inoculated. Modelling from Sage suggests that relaxing restrictions after the top nine priority groups are vaccinated would put daily Covid-19 deaths near zero, so long as vaccines cut transmission by half.
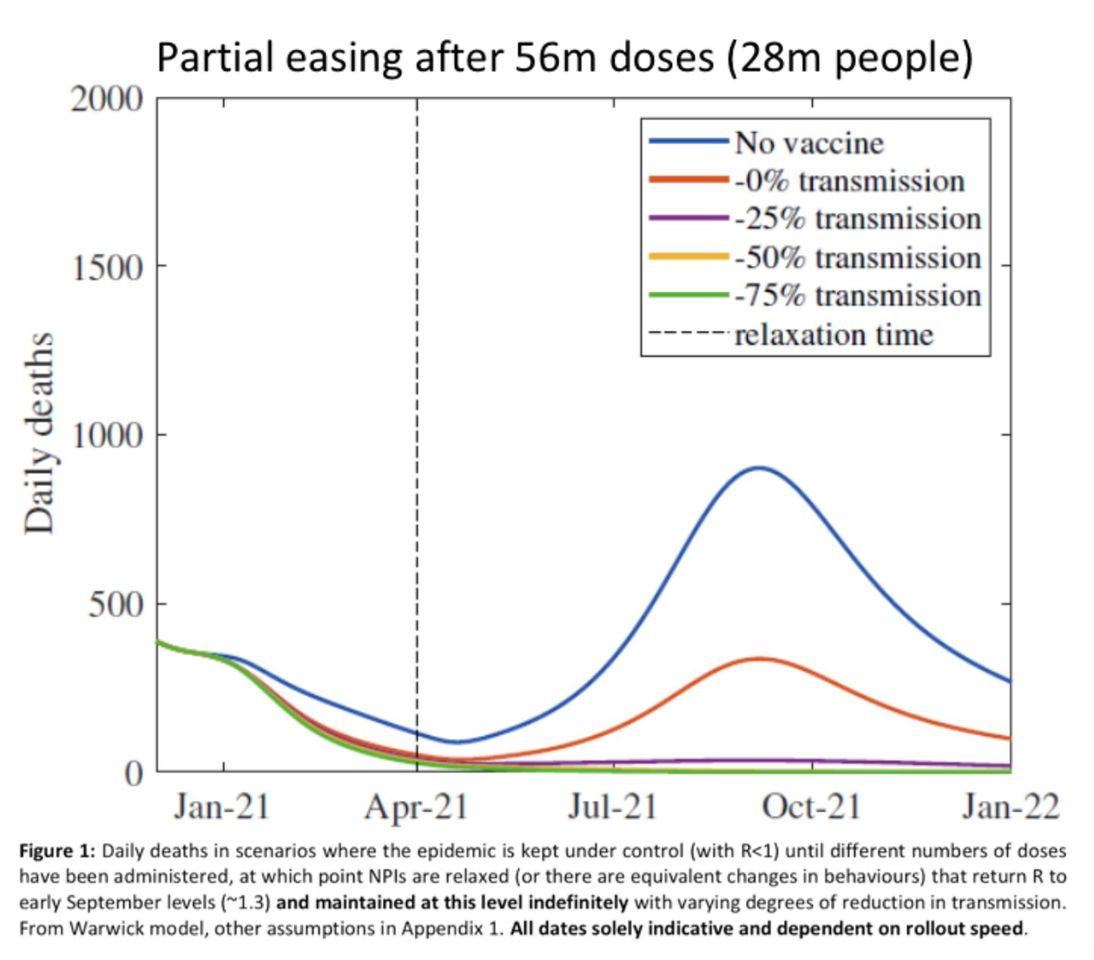
There is a catch, however. Sage’s modelling still assumes September-style restrictions; that is, social distancing rules affecting businesses and people’s personal lives. There are two questions for ministers: first, how quickly can they get the rest of the adult population vaccinated? The second, even more difficult question to answer, is how low do rates of hospitalisations and deaths have to fall before the government will meaningfully reopen society?
Last month, Matt Hancock told The Spectator that once the vulnerable were inoculated, the country would ‘cry freedom’. But tolerance for risk is fundamentally a political decision that this government has not even begun to address. And there’s no doubt that whatever criteria it sets will be challenged by opposition parties. The Covid-19 crisis has always been about trade-offs and difficult decision-making — coming out of this crisis will be no exception.











